Nivalenol
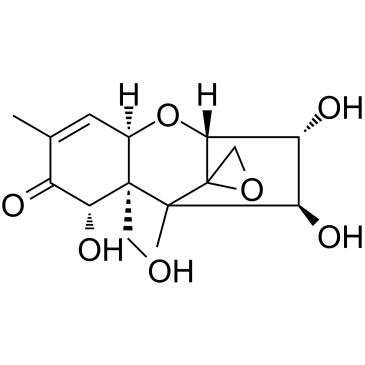
Nivalenol structure
|
Common Name | Nivalenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23282-20-4 | Molecular Weight | 312.315 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 585.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O7 | Melting Point | 222-223ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 221.9±23.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Low toxicity of deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in microbial cells.
Toxins (Basel.) 7(1) , 187-200, (2015) Host plants excrete a glucosylation enzyme onto the plant surface that changes mycotoxins derived from fungal secondary metabolites to glucosylated products. Deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside (DON3G) is synthesized by grain uridine diphosphate-glucosyltransferase, a... |
|
|
Toxicity induced by F. poae-contaminated feed and the protective effect of Montmorillonite supplementation in broilers.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 74 , 120-30, (2014) The T-2 and HT-2 toxins, the main metabolites of Fusarium poae, induce toxicity in broilers and accumulate in tissues. Consequently, during the breeding process of broilers, diets are frequently supplemented with physical adsorbents to protect birds against t... |
|
|
Pathogenicity, symptom development, and mycotoxin formation in wheat by Fusarium species frequently isolated from sugar beet.
Phytopathology 101(11) , 1338-45, (2011) Crop rotations with putative non-host crops such as sugar beet are often recommended to reduce Fusarium head blight (FHB) in cereals. However, recent observations have shown pathogenic, endophytic, and saprotrophic colonization of sugar beet with various Fusa... |
|
|
Structure and conformational dynamics of trichothecene mycotoxins.
J. Nat. Prod. 71 , 589-94, (2008) A combination of NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling has been employed to characterize the conformation and dynamics of the macrolide ring in verrucarin A and roridin A, two closely related toxins in the trichothecene mycotoxin family. Longitudinal carbon... |
|
|
3D QSAR study of the toxicity of trichothecene mycotoxins.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44 , 4485-9, (2009) Trichothecene mycotoxins, toxic natural products of fungi from the family Hypocreaceae, are potent inhibitors of protein synthesis. The application of 3D QSAR to these toxins explored the structural basis for their biological activities. A CoMFA (Q(2)=0.619, ... |
|
|
Occurrence and distribution of 13 trichothecene toxins in naturally contaminated maize plants in Germany.
Toxins (Basel.) 4(10) , 778-87, (2012) The objective of the present study was to monitor the occurrence and distribution of a spectrum of trichothecene toxins in different parts of maize plants. Therefore maize plants were sampled randomly from 13 fields in southwest Germany and the fractions kern... |
|
|
Molecular survey of trichothecene genotypes of Fusarium graminearum species complex from barley in southern Brazil.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 148(3) , 197-201, (2011) Fusarium head blight is a disease of primary concern to small-grain cereals of Brazil, including barley. Its main causal agent, Fusarium graminearum species complex (Fg complex)¸ is able to produce mycotoxins, especially deoxynivalenol (DON) and nivalenol (NI... |
|
|
New insights into mycotoxin mixtures: the toxicity of low doses of Type B trichothecenes on intestinal epithelial cells is synergistic.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 272(1) , 191-8, (2013) Deoxynivalenol (DON) is the most prevalent trichothecene mycotoxin in crops in Europe and North America. DON is often present with other type B trichothecenes such as 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol (3-ADON), 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol (15-ADON), nivalenol (NIV) and fusa... |
|
|
Genotyping and phenotyping of Fusarium graminearum isolates from Germany related to their mycotoxin biosynthesis.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 151(1) , 78-86, (2011) Fusarium graminearum is the most important pathogen causing Fusarium head blight (FHB) of small cereal grains worldwide responsible for quantitative and qualitative yield losses. The presence in crops is often associated with mycotoxin contamination of foodst... |
|
|
Comparison of murine anorectic responses to the 8-ketotrichothecenes 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol, 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol, fusarenon X and nivalenol
Food Chem. Toxicol. 50(6) , 2056-61, (2012) Highlights ► We compare the anorectic effects of 3-ADON, 15- ADON, NIV, FX to those of DON. ► Like DON, 3-ADON and 15-ADON induce transient anorexia. ► FX and NIV induce much longer, persistent anorectic effects than DON or the ADONs. ► IP exposures to tricho... |