| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
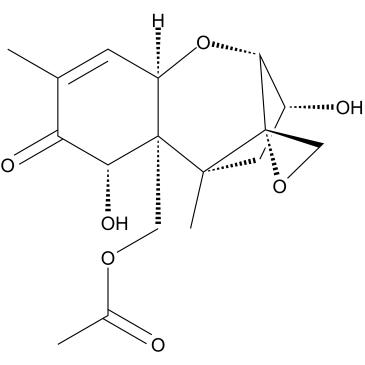 |
15-Acetyl-deoxynivalenol
CAS:88337-96-6 |
|
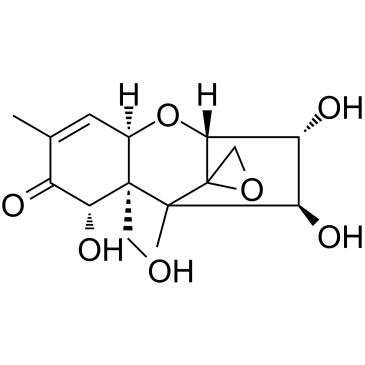 |
Nivalenol
CAS:23282-20-4 |
|
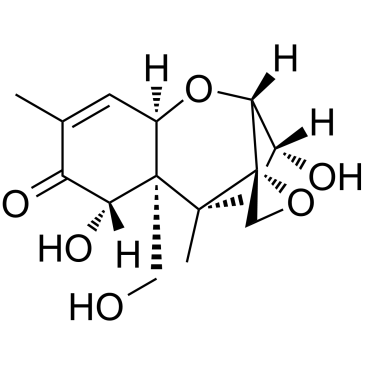 |
DEOXYNIVALENOL
CAS:51481-10-8 |
|
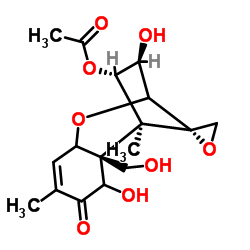 |
Fusarenon-X
CAS:23255-69-8 |