双去甲氧基姜黄素
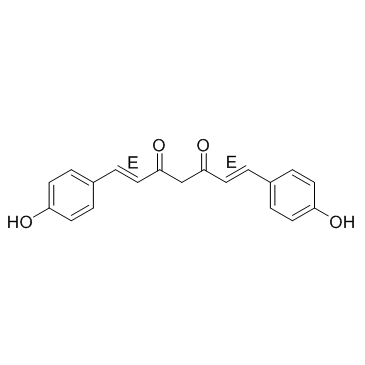
双去甲氧基姜黄素结构式

|
常用名 | 双去甲氧基姜黄素 | 英文名 | Bisdemethoxycurcumin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 33171-05-0 | 分子量 | 308.328 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 551.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C19H16O4 | 熔点 | 221-223ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 301.3±25.2 °C |
|
An efficient and economical MTT assay for determining the antioxidant activity of plant natural product extracts and pure compounds.
J. Nat. Prod. 73 , 1193-5, (2010) Antioxidants scavenge free radicals, singlet oxygen, and electrons in cellular redox reactions. The yellow MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] is reduced to a purple formazan by mitochondrial enzymes. NADPH is the basis of esta... |
|
|
Molecularly imprinted polymers for cleanup and selective extraction of curcuminoids in medicinal herbal extracts.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407(3) , 803-12, (2015) This paper describes the synthesis of novel molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), prepared by a noncovalent imprinting approach, for cleanup and preconcentration of curcumin (CUR) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC) from medicinal herbal extracts and further ana... |
|
|
Isoxazole analogs of curcuminoids with highly potent multidrug-resistant antimycobacterial activity.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45 , 4446-57, (2010) Curcumin (1), demethoxycurcumin (2) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (3), the curcuminoid constituents of the medicinal plant Curcuma longa L., have been structurally modified to 55 analogs and antimycobacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis has been ev... |
|
|
Significant enhancement in radical-scavenging activity of curcuminoids conferred by acetoxy substituent at the central methylene carbon.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 3793-800, (2011) For a compound to be a radical-trapping antioxidant, the antioxidant-derived radical must be sufficiently inert to molecular oxygen as this would generate harmful chain-propagating peroxyl radicals. Curcumin has a unique structure with phenolic hydroxyl group... |
|
|
Identification of curcumin derivatives as human glyoxalase I inhibitors: A combination of biological evaluation, molecular docking, 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamics simulation studies.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 1189-96, (2011) Several recent developments suggest that the human glyoxalase I (GLO I) is a potential target for anti-tumor drug development. In present study, a series of curcumin derivatives with high inhibitory activity against human GLO I were discovered. Inhibition con... |
|
|
Curcumin modulates efflux mediated by yeast ABC multidrug transporters and is synergistic with antifungals.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 , 3256-65, (2009) Curcumin (CUR), a natural product of turmeric, from rhizomes of Curcuma longa, is a known agent of reversal of drug resistance phenotypes in cancer cells overexpressing ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, viz., ABCB1, ABCG2, and ABCC1. In the present stu... |
|
|
Efficiency of foam fractionation for the enrichment of nonpolar compounds from aqueous extracts of plant materials.
J. Nat. Prod. 68 , 1386-9, (2005) Biologically active compounds from several useful plants were enriched using foam fractionation, a separatory method belonging to the adsorptive bubble separation (ABS). Nonpolar humulones (1-6) from Pilsener beer, curcuminoids (7-9) from turmeric, and carote... |
|
|
A labdane diterpene glucoside from the rhizomes of Curcuma mangga.
J. Nat. Prod. 68 , 1090-3, (2005) A new labdane diterpene glucoside, curcumanggoside (1), together with nine known compounds, including labda-8(17),12-diene-15,16-dial (2), calcaratarin A (3), zerumin B (4), scopoletin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4,6-h... |
|
|
Curcuminoid analogs with potent activity against Trypanosoma and Leishmania species.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45 , 941-56, (2010) The natural curcuminoids curcumin (1), demethoxycurcumin (2) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (3) have been chemically modified to give 46 analogs and 8 pairs of 1:1 mixture of curcuminoid analogs and these parent curcuminoids and their analogs were assessed against ... |
|
|
Structural investigation into the inhibitory mechanisms of indomethacin and its analogues towards human glyoxalase I.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 4243-7, (2011) In the present work, a combined study of kinetic analysis, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations on indomethacin and its analogues is performed to better understand their inhibitory mechanisms towards human glyoxalase I (GLOI). A remarkable co... |