| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
酮洛芬
CAS:22071-15-4 |
|
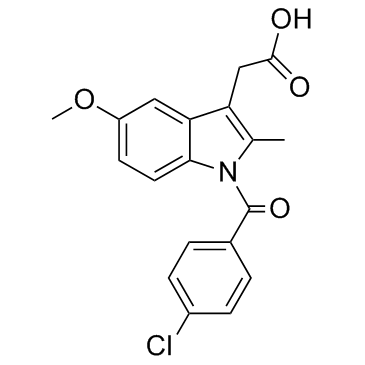 |
吲哚美辛
CAS:53-86-1 |
|
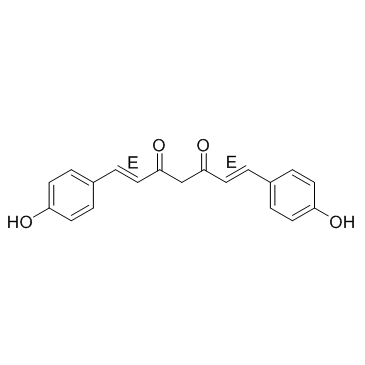 |
双去甲氧基姜黄素
CAS:33171-05-0 |