吲哚美辛
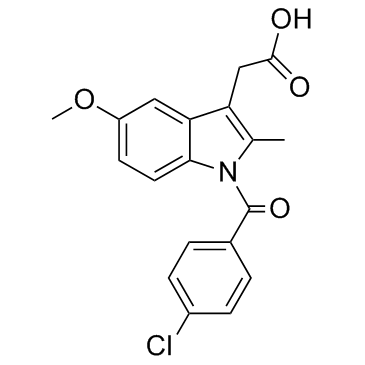
吲哚美辛结构式

|
常用名 | 吲哚美辛 | 英文名 | Indometacin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 53-86-1 | 分子量 | 357.78800 | |
| 密度 | 1.32g/cm3 | 沸点 | 499.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C19H16ClNO4 | 熔点 | 155-162 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 255.8ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS06 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Mechanical stimulation of human tendon stem/progenitor cells results in upregulation of matrix proteins, integrins and MMPs, and activation of p38 and ERK1/2 kinases.
BMC Mol. Biol. 16 , 6, (2015) Tendons are dense connective tissues subjected periodically to mechanical stress upon which complex responsive mechanisms are activated. These mechanisms affect not only the development of these tissues but also their healing. Despite of the acknowledged impo... |
|
|
Increased antidepressant sensitivity after prefrontal cortex glucocorticoid receptor gene deletion in mice.
Physiol. Behav. 138 , 113-7, (2014) Our laboratory has previously shown that antidepressants regulate glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression in the prefrontal cortex (PFC). To determine if PFC GR are involved in antidepressant effects on behavior or hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) ... |
|
|
Growth and functional harvesting of human mesenchymal stromal cells cultured on a microcarrier-based system.
Biotechnol. Prog. 30(4) , 889-95, (2014) Human mesenchymal stromal cells (hMSCs) cells are attractive for applications in tissue engineering and cell therapy. Because of the low availability of hMSCs in tissues and the high doses of hMSCs necessary for infusion, scalable and cost-effective technolog... |
|
|
Indomethacin inhibits activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the rat kidney: possible role of this effect in the pathogenesis of indomethacin-induced renal damage.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 221 , 77-87, (2014) The clinical use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is often associated with adverse effects in the kidney. Indomethacin, an NSAID that has been shown to induce oxidative stress in the kidney, was used to study the pathogenesis of renal damage ... |
|
|
Differentiation of Schwann‑like cells from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.
Mol. Med. Report. 11(2) , 1146-52, (2014) The use of artificial nerves for the repair of peripheral nerve defects is restricted by the limited sources of Schwann cells (SCs). Human mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)‑derived Schwann‑like cells are considered an alternative and desirable cell source. The aim ... |
|
|
Validation of cyclooxygenase-2 as a direct anti-inflammatory target of 4-O-methylhonokiol in zymosan-induced animal models.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 38 , 813-25, (2015) 4-O-methylhonokiol (MH) is known to inhibit inflammation by partially understood mechanisms. Here, the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of MH were examined using enzymatic, cellular, and animal assays. In enzymatic assays, MH inhibited COX-2 activity with an IC50... |
|
|
Intercellular transfer of messenger RNAs in multiorgan tumorigenesis by tumor cell-derived exosomes.
Mol. Med. Report. 11 , 4657-63, (2015) Exosomes are small membrane vesicles of endocytic origin. They are derived from various cells, including tumor cells, and may serve as important modulators of intercellular communication. The present study established a U‑87 MG human glioblastoma cell line th... |
|
|
Polyunsaturated fatty acids influence differential biosynthesis of oxylipids and other lipid mediators during bovine coliform mastitis.
J. Dairy Sci. 98 , 6202-15, (2015) Coliform mastitis is a severe and sometimes fatal disease characterized by an unregulated inflammatory response. The initiation, progression, and resolution of inflammatory responses are regulated, in part, by potent oxylipid metabolites derived from polyunsa... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Mechanisms involved in the gastroprotective activity of Celtis iguanaea (Jacq.) Sargent on gastric lesions in mice.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 155(3) , 1616-24, (2014) Celtis iguanaea (Canabaceae) is popularly known as esporão-de-galo, stands out among the medicinal plants used for treatment of gastric ulcers. In Brazil, the leaves they are used traditionally in infusion forms as an analgesic, antiasthmatic, digestive and d... |