| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
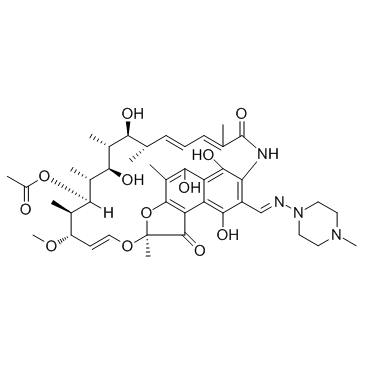 |
利福平
CAS:13292-46-1 |
|
 |
异烟肼
CAS:54-85-3 |
|
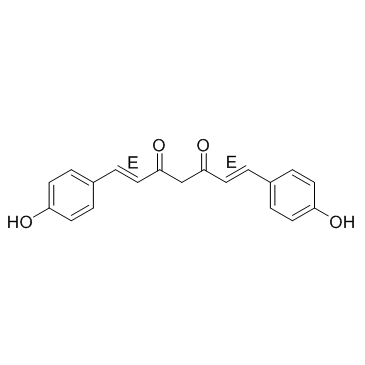 |
双去甲氧基姜黄素
CAS:33171-05-0 |