| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
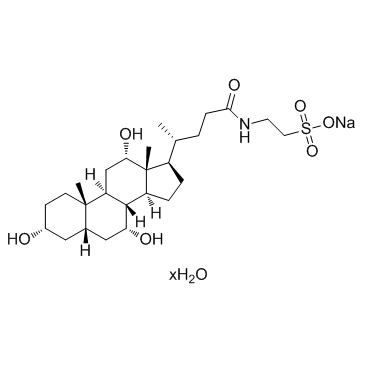 |
Taurocholic acid sodium salt hydrate
CAS:345909-26-4 |
|
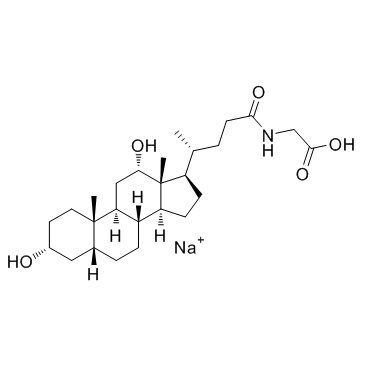 |
Glycodeoxycholate Sodium
CAS:16409-34-0 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
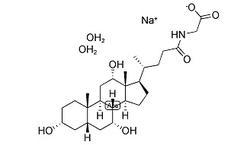 |
SodiuM glycocholate hydrate
CAS:338950-81-5 |
|
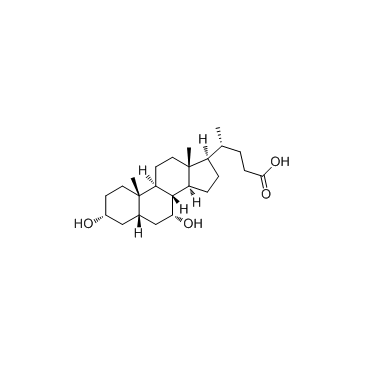 |
Chenodeoxycholic acid
CAS:474-25-9 |
|
 |
Sodium cholate
CAS:206986-87-0 |
|
 |
Sodium chenodeoxycholate
CAS:2646-38-0 |
|
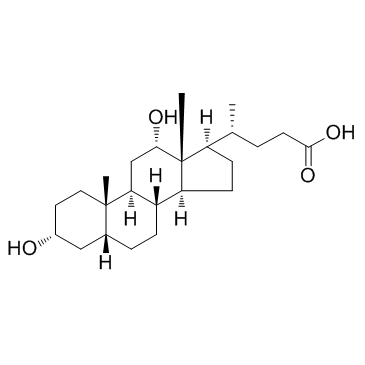 |
Deoxycholic acid
CAS:83-44-3 |
|
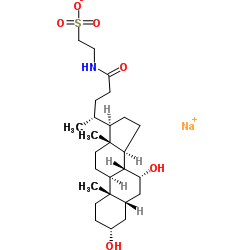 |
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid sodium salt
CAS:6009-98-9 |
|
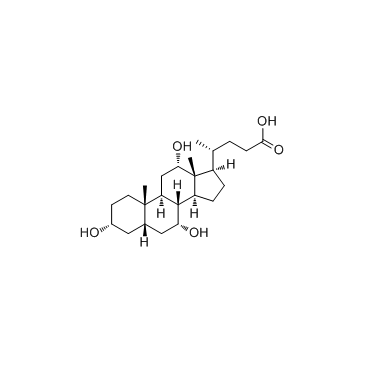 |
cholic acid
CAS:81-25-4 |