cholic acid
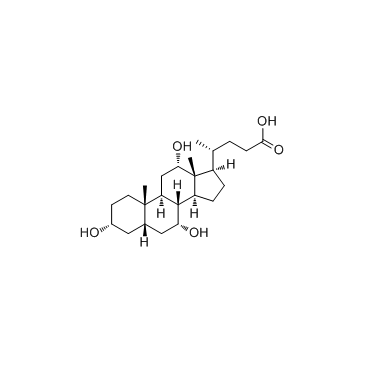
cholic acid structure
|
Common Name | cholic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 81-25-4 | Molecular Weight | 408.571 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 583.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O5 | Melting Point | 197-202 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 321.0±26.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Tunable stringency aptamer selection and gold nanoparticle assay for detection of cortisol.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 406(19) , 4637-47, (2014) The first-known aptamer for the stress biomarker cortisol was selected using a tunable stringency magnetic bead selection strategy. The capture DNA probe immobilized on the beads was systematically lengthened to increase the number of bases bound to the compl... |
|
|
Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of the major tripartite multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli: functional conservation in disparate animal reservoirs despite exposure to antimicrobial chemotherapy.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 1007-15, (2010) AcrAB-TolC imparts a strong intrinsic resistance phenotype to many clinically significant molecules in Escherichia coli. This complex is composed of a pump, AcrB, and a periplasmic protein, AcrA, that exports substrates through a common outer membrane porin, ... |
|
|
Substrate competition studies using whole-cell accumulation assays with the major tripartite multidrug efflux pumps of Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 923-9, (2007) AcrAB-TolC is the major, constitutively expressed tripartite multidrug efflux system in Escherichia coli that recognizes various structurally unrelated molecules, including many antibiotics, dyes, and steroids. The AcrB inner membrane pump portion of the effl... |
|
|
Cholic acid for hepatic steatosis in patients with lipodystrophy: a randomized, controlled trial.
Eur. J. Endocrinol. 168(5) , 771-8, (2013) Hepatic steatosis is a common complication in patients with lipodystrophies and can lead to cirrhosis. There is no proven effective therapy for hepatic steatosis, but cholic acid (CA), a farnesoid X receptor agonist, has previously been shown to reduce hepati... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
An UPLC-MS/MS method for quantitative profiling of bile acids in sea lamprey plasma and tissues.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 980 , 72-8, (2015) Bile acids (BAs) have recently gained more attention because of their diverse roles from digestion to signaling. Simultaneous analyses of various BAs in biological samples are challenging due to their structural similarity, relatively low concentrations, and ... |
|
|
A possible role of chenodeoxycholic acid and glycine-conjugated bile acids in fibrotic steatohepatitis in a dietary rat model.
Dig. Dis. Sci. 59(7) , 1490-501, (2014) Our previous study indicated that hepatic bile acids (BAs) may have deposited and stimulated the pathogenesis of a high fat-cholesterol (HFC) diet-induced fibrotic steatohepatitis in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive 5/Dmcr rats, based on dysregulated B... |
|
|
New method for the determination of bile acids in human plasma by liquid-phase microextraction using liquid chromatography-ion-trap-time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1388 , 102-9, (2015) Bile acids (BAs) are derived from cholesterol and produced in the liver. The most abundant bile acids in humans are usually conjugated with glycine and taurine and are divided into primary BAs such as cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and seco... |
|
|
A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based method for the simultaneous determination of hydroxy sterols and bile acids.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1371 , 184-95, (2014) Recently, hydroxy sterols and bile acids have gained growing interest as they are important regulators of energy homoeostasis and inflammation. The high number of different hydroxy sterols and bile acid species requires powerful analytical tools to quantify t... |
|
|
A metabonomic study of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
Mol. Biosyst. 10(10) , 2617-25, (2014) Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory and autoimmune disease accompanied by the destruction and deformities of joints. Adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) is one of the excellent animal models of RA used to understand disease pathogenesis ... |