cholic acid
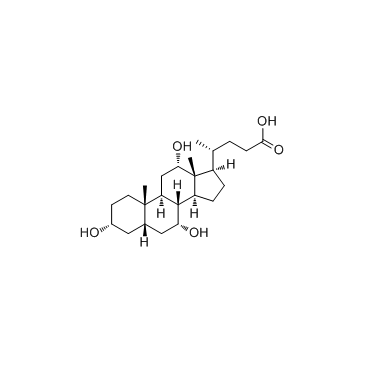
cholic acid structure
|
Common Name | cholic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 81-25-4 | Molecular Weight | 408.571 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 583.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O5 | Melting Point | 197-202 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 321.0±26.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of cholic acidCholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. |
| Name | cholic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cholic acid is a major primary bile acid produced in the liver and usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Cholic acid competitively binds Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) on HepG2 cells and significantly inhibits the uptake of Cholic acid (CA)-nanoliposomes (LPs)-Doxorubicin (DOX)-HCl, which indicates that CA-LPs-DOX-HCl are also uptaken via NTCP-mediated endocytosis pathway[1]. |
| In Vivo | Cholic acid feeding leads to increased CYP2D6 expression in CYP2D6-humanized mice. As a cholestasis model, Tg-CYP2D6 mice are fed a Cholic acid (CA)-supplemented diet for over 1 week. The treatment is known to increase bile acid pool size by 2-fold and to replace ~90% of bile acids with CA, recapitulating the features of cholestatic conditions in humans[2]. |
| Cell Assay | HepG2 cells are pretreated with the inhibitors NaN3 (1 mg/mL), Genistein (50 μg/mL), MβCD (10 mM), Nystatin (50 μg/mL), Chlorpromazine (10 μg/mL), and Cholic acid (1 mg/mL) for 30 min. After removing the inhibitors, the cells are incubated with CA-LPs for 2 h, and the cellular uptake of LPs is determined in the "In vitro cellular uptake assays" section[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Tg-CYP2D6 mice are fed with normal chow (control) or 1% (w/w) Cholic acid-supplemented diet (CA) for 14 days (n=4 mice/group). Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities are measured in mouse serum. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 583.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 197-202 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 408.571 |
| Flash Point | 321.0±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 408.287567 |
| PSA | 97.99000 |
| LogP | 2.62 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | 0.28 g/L (15 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | FZ9350000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
Tunable stringency aptamer selection and gold nanoparticle assay for detection of cortisol.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 406(19) , 4637-47, (2014) The first-known aptamer for the stress biomarker cortisol was selected using a tunable stringency magnetic bead selection strategy. The capture DNA probe immobilized on the beads was systematically le... |
|
|
Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of the major tripartite multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli: functional conservation in disparate animal reservoirs despite exposure to antimicrobial chemotherapy.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 1007-15, (2010) AcrAB-TolC imparts a strong intrinsic resistance phenotype to many clinically significant molecules in Escherichia coli. This complex is composed of a pump, AcrB, and a periplasmic protein, AcrA, that... |
|
|
Substrate competition studies using whole-cell accumulation assays with the major tripartite multidrug efflux pumps of Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 923-9, (2007) AcrAB-TolC is the major, constitutively expressed tripartite multidrug efflux system in Escherichia coli that recognizes various structurally unrelated molecules, including many antibiotics, dyes, and... |
| Cholalic acid |
| Cholan-24-oic acid, 3,7,12-trihydroxy-, (3α,5β,7α,12α)- (9CI) |
| cholic acid |
| 17b-(1-Methyl-3-carboxypropyl)etiocholane-3a,7a,12a-triol |
| 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxycholanic acid |
| 5β-Cholic acid |
| 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholanoic acid |
| (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-Trihydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid |
| 5b-Cholic acid |
| 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholanic Acid |
| 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid |
| CHOLALIN |
| MFCD00003672 |
| Cholan-24-oic acid, 3,7,12-trihydroxy-, (3α,5β,7α,8ξ,12α,20R)- |
| EINECS 201-337-8 |
| Cholbam |
| Cholic&Cyclosphorine |
| 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-b-cholanic acid |
| 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-β-cholanic acid |
| Cholic acd |
| 5b-Cholanic acid-3a,7a,12a-triol |
| AHR 3053-13C3 |
| (3α,5β,7α,12α)-3,7,12-Trihydroxycholan-24-oic acid |
| 3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholan-24-oic Acid |
| 5β-Cholanic acid, 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy- (7CI) |
| CHOLATE |
| Kolbam |
| UNII-G1JO7801AE |
| Orphacol |
| Cholic acid, 5β- |
| (3a,5b,7a,12a)-3,7,12-Trihydroxycholan-24-oic acid |
| Cholan-24-oic acid, 3,7,12-trihydroxy-, (3α,5β,7α,12α)- |
| Cholan-24-oic acid, 3,7,12-trihydroxy-, (3-α,5-β,7-α,12-α)- |
| (3α,5β,7α,8ξ,12α,20R)-3,7,12-Trihydroxycholan-24-oic acid |
 CAS#:911-40-0
CAS#:911-40-0 CAS#:434-13-9
CAS#:434-13-9 CAS#:850210-60-5
CAS#:850210-60-5 CAS#:850210-62-7
CAS#:850210-62-7 CAS#:1448-36-8
CAS#:1448-36-8 CAS#:122752-67-4
CAS#:122752-67-4 CAS#:105730-97-0
CAS#:105730-97-0 CAS#:863-57-0
CAS#:863-57-0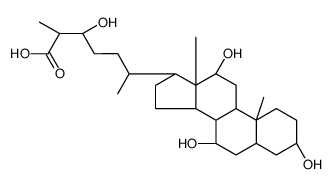 CAS#:1061-64-9
CAS#:1061-64-9![methyl (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-12-oxo-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/091/10538-64-4.png) CAS#:10538-64-4
CAS#:10538-64-4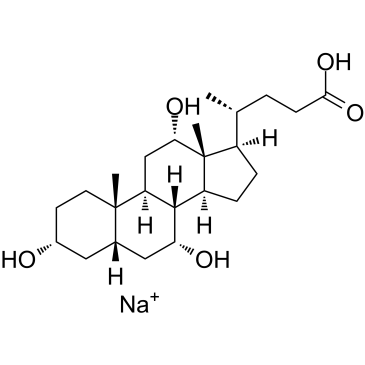 CAS#:361-09-1
CAS#:361-09-1 CAS#:4651-67-6
CAS#:4651-67-6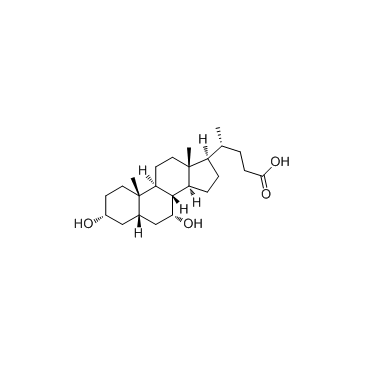 CAS#:474-25-9
CAS#:474-25-9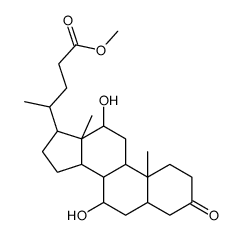 CAS#:14772-99-7
CAS#:14772-99-7![(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S)-17-[(2R)-6-hydroxy-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,7,12-triol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/186/18866-87-0.png) CAS#:18866-87-0
CAS#:18866-87-0![methyl 3alpha-[(ethoxycarbonyl)oxy]-7,12-dioxo-5beta-cholan-24-oate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/052/21059-42-7.png) CAS#:21059-42-7
CAS#:21059-42-7
