| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
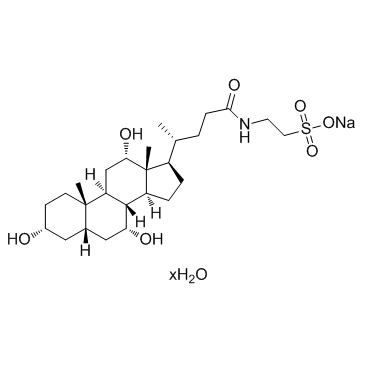 |
牛磺胆酸钠盐 水合
CAS:345909-26-4 |
|
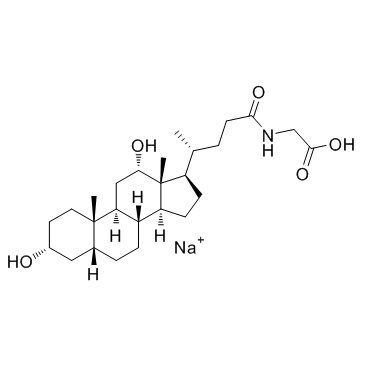 |
甘氨脱氧胆酸钠
CAS:16409-34-0 |
|
 |
L-谷氨酰胺
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
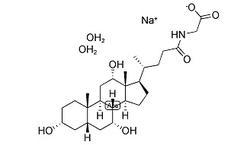 |
甘胆酸钠水合物
CAS:338950-81-5 |
|
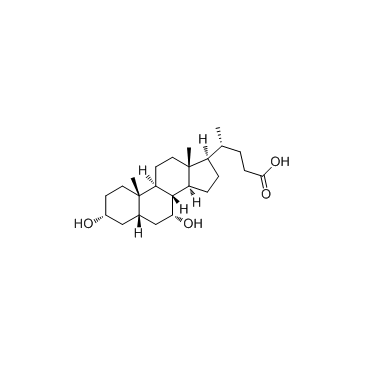 |
鹅去氧胆酸; 鹅脱氧胆酸
CAS:474-25-9 |
|
 |
胆酸钠
CAS:206986-87-0 |
|
 |
鹅去氧胆酸钠
CAS:2646-38-0 |
|
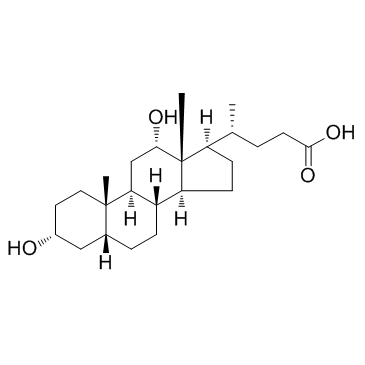 |
去氧胆酸
CAS:83-44-3 |
|
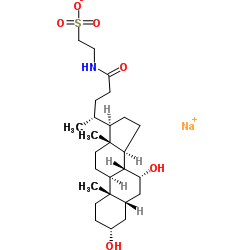 |
牛磺鹅去氧胆酸钠
CAS:6009-98-9 |
|
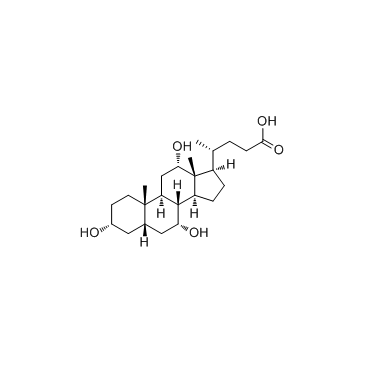 |
胆酸
CAS:81-25-4 |