Chenodeoxycholic acid
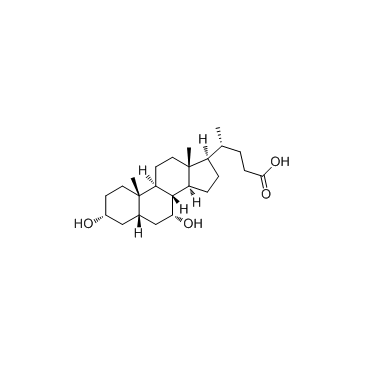
Chenodeoxycholic acid structure
|
Common Name | Chenodeoxycholic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 474-25-9 | Molecular Weight | 392.572 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 547.1±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O4 | Melting Point | 165-167 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 298.8±19.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Transcriptional Regulation of Cytosolic Sulfotransferase 1C2 by Intermediates of the Cholesterol Biosynthetic Pathway in Primary Cultured Rat Hepatocytes.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 355 , 429-41, (2015) Cytosolic sulfotransferase 1C2 (SULT1C2) is expressed in the kidney, stomach, and liver of rats; however, the mechanisms regulating expression of this enzyme are not known. We evaluated transcriptional regulation of SULT1C2 by mevalonate (MVA)-derived interme... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Ultra high resolution SFC-MS as a high throughput platform for metabolic phenotyping: application to metabolic profiling of rat and dog bile.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 966 , 200-7, (2014) Ultra high resolution SFC-MS (on sub-2μm particles) coupled to mass spectrometry has been evaluated for the metabolic profiling of rat and dog bile. The selectivity of the SFC separation differed from that seen in previous reversed-phase UPLC-MS studies on bi... |
|
|
An UPLC-MS/MS method for quantitative profiling of bile acids in sea lamprey plasma and tissues.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 980 , 72-8, (2015) Bile acids (BAs) have recently gained more attention because of their diverse roles from digestion to signaling. Simultaneous analyses of various BAs in biological samples are challenging due to their structural similarity, relatively low concentrations, and ... |
|
|
A possible role of chenodeoxycholic acid and glycine-conjugated bile acids in fibrotic steatohepatitis in a dietary rat model.
Dig. Dis. Sci. 59(7) , 1490-501, (2014) Our previous study indicated that hepatic bile acids (BAs) may have deposited and stimulated the pathogenesis of a high fat-cholesterol (HFC) diet-induced fibrotic steatohepatitis in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive 5/Dmcr rats, based on dysregulated B... |
|
|
Integrating multiple omics to unravel mechanisms of Cyclosporin A induced hepatotoxicity in vitro.
Toxicol. In Vitro 29(3) , 489-501, (2015) In order to improve attrition rates of candidate-drugs there is a need for a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying drug-induced hepatotoxicity. We aim to further unravel the toxicological response of hepatocytes to a prototypical cholestatic compo... |