Pinoresinol
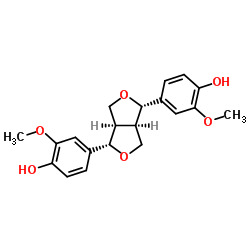
Pinoresinol structure
|
Common Name | Pinoresinol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 487-36-5 | Molecular Weight | 358.385 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 556.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H22O6 | Melting Point | 121 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 290.4±30.1 °C | |
|
Characterisation and phenolic profiles of two rare olive oils from southern Tunisia: Dhokar and Gemri-Dhokar cultivars.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 93(3) , 527-34, (2013) The aim of this work was to study the chemical characteristics of two Tunisian cultivars, namely Dhokar and Gemri-Dhokar, to analyse the fatty acids, sterols, triacylglycerols, triterpenic alcohols, and to determine the phenolic composition and oxidative stab... |
|
|
[Study on the chemical constituents of the roots of Dendropanax chevalieri].
Zhong Yao Cai 35(1) , 62-4, (2012) To study the chemical constituents of the roots of Dendropanax chevalieri.The constituents were isolated by column chromatography with silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 gel and RP-18. Their structures were elucidated by analysis of spectral data and physicochemical ... |
|
|
[Chemical constituents of the roots of Vaccinium bracteatum].
Zhong Yao Cai 35(6) , 917-9, (2012) To study the chemical constituents of the roots of Vaccinium bracteatum.The constituents were separated and purified with chromatographic methods (including silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 and RP-18 column chromatography), and their structures were determined by s... |
|
|
Phenolic Profiling of Olives and Olive Oil Process-Derived Matrices Using UPLC-DAD-ESI-QTOF-HRMS Analysis.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 3859-72, (2015) All of the matrices entailed in olive oil processing were screened for the presence of known and new phenol constituents in a single study, combining an ultra high pressure liquid chromatography system with diode array and electrospray ionization quadrupole t... |
|
|
[Non-alkaloid chemical constituents from Coptis chinensis].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 37(9) , 1241-4, (2012) To separate and identify chemical constituents from Coptis chinensis.The compounds were separated and purified by various chromatographic techniques. Their structures were identified on the basis of their physicochemical properties using spectral techniques s... |
|
|
Simiranes A and B: erythroxylanes diterpenes and other compounds from Simira eliezeriana (Rubiaceae).
Nat. Prod. Res. 25(18) , 1713-9, (2011) The first phytochemical study of Simira eliezeriana Peixoto (Rubiaceae) allowed the isolation and structural determination of two new diterpenes named simirane A [(5R,6R,8R,9R,10S,11S,13S)-6β,11β-dihydroxy-2,4(18),15-erythroxylatrien-1-one] (1) and simirane B... |
|
|
PPARγ agonist from Chromolaena odorata.
J. Nat. Prod. 75(12) , 2076-81, (2012) A phytochemical investigation of Chromolaena odorata resulted in the isolation of five new compounds, 5aα,6,9,9aβ,10-pentahydro-10β-hydroxy-7-methylanthra[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-5-one (1), 1,2-methylenedioxy-6-methylanthraquinone (2), 3-hydroxy-1,2,4-trimethoxy-6-... |
|
|
Among plant lignans, pinoresinol has the strongest antiinflammatory properties in human intestinal Caco-2 cells.
J. Nutr. 142 , 1798-1805, (2012) Dietary lignans show some promising health benefits, but little is known about their fate and activities in the small intestine. The purpose of this study was thus to investigate whether plant lignans are taken up by intestinal cells and modulate the intestin... |
|
|
Intake of the plant lignans matairesinol, secoisolariciresinol, pinoresinol, and lariciresinol in relation to vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in middle age-elderly men and post-menopausal women living in Northern Italy.
Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20(1) , 64-71, (2010) It has been suggested that lignan intake may decrease the risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) by modifying traditional risk factors as well as aortic stiffness. However, the role of dietary lignans on the vascular system is largely unknown. The objective wa... |
|
|
Abscisic acid regulates pinoresinol-lariciresinol reductase gene expression and secoisolariciresinol accumulation in developing flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) seeds.
Planta 235 , 85-98, (2012) Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), the main phytoestrogenic lignan of Linum usitatissimum, is accumulated in the seed coat of flax during its development and pinoresinol-lariciresinol reductase (PLR) is a key enzyme in flax for its synthesis. The promote... |