| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
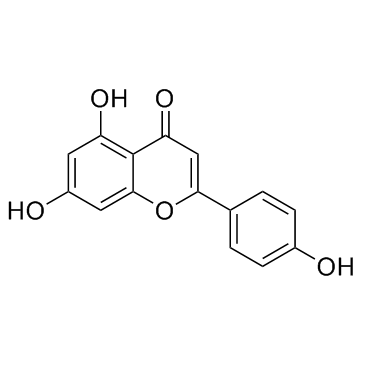 |
Apigenin
CAS:520-36-5 |
|
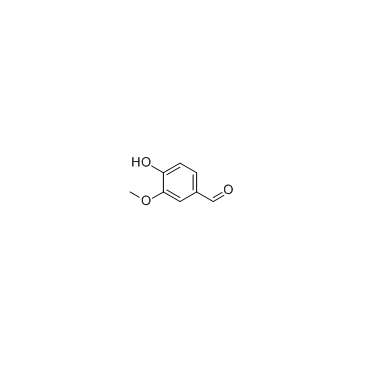 |
Vanillin
CAS:121-33-5 |
|
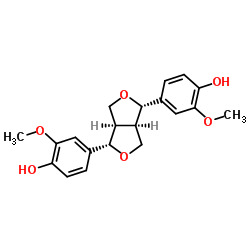 |
Pinoresinol
CAS:487-36-5 |
|
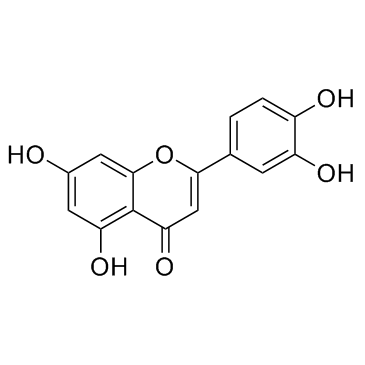 |
Luteolin
CAS:491-70-3 |
|
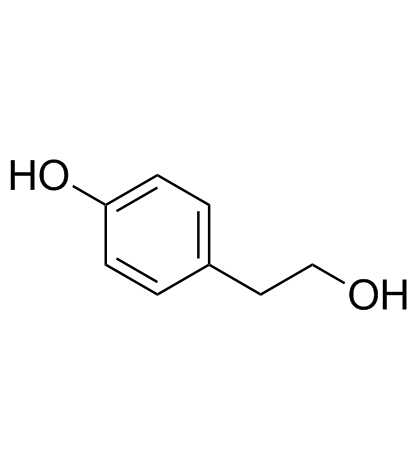 |
4-Hydroxyphenyl ethanol
CAS:501-94-0 |
|
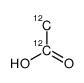 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
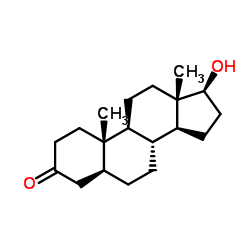 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |