Cupferron
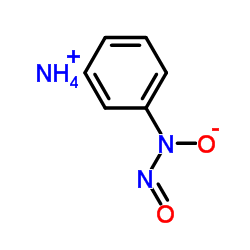
Cupferron structure
|
Common Name | Cupferron | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 135-20-6 | Molecular Weight | 155.155 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 243.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9N3O2 | Melting Point | 150-155 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 101.3ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Intermediate analogue inhibitors of mandelate racemase: N-Hydroxyformanilide and cupferron.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 , 105-8, (2007) Mandelate racemase (MR) catalyzes the 1,1-proton transfer that interconverts the enantiomers of mandelate. The transition state/intermediate analogues N-hydroxyformanilide (K(i)=2.79+/-0.19 microM) and cupferron (K(i)=2.67+/-0.09 microM) are identified as pot... |
|
|
Celecoxib prodrugs possessing a diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate nitric oxide donor moiety: synthesis, biological evaluation and nitric oxide release studies.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 , 4544-9, (2010) A new class of anti-inflammatory (AI) cupferron prodrugs was synthesized wherein a diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolato ammonium salt, and its O(2)-methyl and O(2)-acetoxyethyl derivatives, nitric oxide (NO) donor moieties were attached directly to an aryl carbon on a ce... |
|
|
Synthesis and characterization of lithium oxonitrate (LiNO).
J. Inorg. Biochem. 118 , 128-33, (2013) The oxonitrate(1-) anion (NO(-)), the one-electron reduction product of nitric oxide and conjugate base of HNO, has not been synthesized and isolated due to the inherent reactivity of this anion. The large scale synthesis and characterization of a stable NO(-... |
|
|
O-Alkylation of cupferron: aiming at the design and synthesis of controlled nitric oxide releasing agents.
J. Org. Chem. 65(14) , 4333-7, (2000) O-Alkylation of N-nitroso-N-phenylhydroxylamine ammonium salt (cupferron) was studied for the synthesis of novel nitric oxide (NO) releasing agents. The alkylation occurred regioselectively at the terminal oxygen, leading to a single product N-(alkyloxy)-N'-p... |
|
|
Generation of nitric oxide by enzymatic oxidation of N-hydroxy-N-nitrosamines.
J. Biol. Chem. 260(7) , 4069-74, (1985) The nitric oxide (N = O) free radical exhibits potent cytocidal, mutagenic and vasodilatory properties. We have examined the hypothesis that the hydroxynitrosamino functionality (see sequence in text), which occurs naturally in antineoplastic and antihyperten... |
|
|
A "dual-function" photocage releasing nitric oxide and an anthrylmethyl cation with a single wavelength light.
Chemistry 15(28) , 6802-6, (2009)
|
|
|
Increased plasma concentrations of palmitoylethanolamide, an endogenous fatty acid amide, affect oxidative damage of human low-density lipoproteins: an in vitro study.
Atherosclerosis 182(1) , 47-55, (2005) Fatty acid ethanolamides (NAEs) are naturally occurring hydrophobic molecules usually present in a very small amount in many mammalian tissues and cells. Moreover, these compounds have been isolated in mammalian biological fluids, such as blood. Palmitoyletha... |
|
|
The reaction of nitroxyl (HNO) with nitrosobenzene gives cupferron (N-nitrosophenylhydroxylamine).
Nitric Oxide 2(1) , 66-72, (1998) Nitroxyl (HNO), a penultimate product in the NOS-catalyzed conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline, generated from Angeli's salt (AS) was determined by trapping it with nitrosobenzene (NB) to produce cupferron. The cupferron thus produced was characterized b... |
|
|
A solvothermal route to ZnO and Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles using the cupferron complex as the precursor.
J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 4(1-2) , 136-40, (2004) ZnO nanoparticles have been synthesized from the cupferron complex by a solvothermal route in toluene solution. The nanoparticles have been prepared in the presence of various capping agents, of which the best results were obtained with tri-n-octylphosphine o... |
|
|
Simultaneous quantification of Bi(III) and U(VI) in environmental water samples with a complicated matrix containing organic compounds.
Environ. Monit. Assess. 185(7) , 5515-22, (2013) Trace amounts of bismuth(III) and uranium(VI) can be simultaneously determined in a single scan by adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry in the presence of cupferron as a complexing agent. Optimal conditions were found to be: 0.1 mol L(-1) acetate buffer ... |