The reaction of nitroxyl (HNO) with nitrosobenzene gives cupferron (N-nitrosophenylhydroxylamine).
F Molano, A Saborido, J Delgado, M Morán, A Megías
Index: Nitric Oxide 2(1) , 66-72, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Nitroxyl (HNO), a penultimate product in the NOS-catalyzed conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline, generated from Angeli's salt (AS) was determined by trapping it with nitrosobenzene (NB) to produce cupferron. The cupferron thus produced was characterized by complexation with Fe3+, Al3+, Cu2+, or Sn2+. UV/VIS spectra of the solubilized (in CHCl3) precipitates formed from NB and nitroxyl generated from AS in the presence of the iron, aluminum, copper, or tin salts were identical to those of their corresponding cupferron complexes. The identities of the Fe3+ and Cu2+ complexes formed from NB and HNO were further confirmed by their identical retention times on HPLC when compared to authentic Fe3+ and Cu2+ cupferron complexes. It was possible to detect 5 x 10(-6) M of the cupferron Fe3+ complex spectrophotometrically and to measure its production from the nitroxyl generators AS and methanesulfohydroxamic acid (MSHA) in the presence of 10(-4) M NB. The yield of cupferron was 51 and 62% of the amount of nitroxyl possible from AS or MSHA, respectively, after taking into account the relative rates of nitroxyl generation from these donors.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
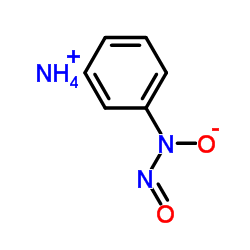 |
Cupferron
CAS:135-20-6 |
C6H9N3O2 |
|
Intermediate analogue inhibitors of mandelate racemase: N-Hy...
2007-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 , 105-8, (2007)] |
|
Celecoxib prodrugs possessing a diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate nit...
2010-08-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 , 4544-9, (2010)] |
|
Synthesis and characterization of lithium oxonitrate (LiNO).
2013-01-01 [J. Inorg. Biochem. 118 , 128-33, (2013)] |
|
O-Alkylation of cupferron: aiming at the design and synthesi...
2000-07-14 [J. Org. Chem. 65(14) , 4333-7, (2000)] |
|
Generation of nitric oxide by enzymatic oxidation of N-hydro...
1985-04-10 [J. Biol. Chem. 260(7) , 4069-74, (1985)] |