3,4,5,6-Tetrachlorobenzene-1,2-diol
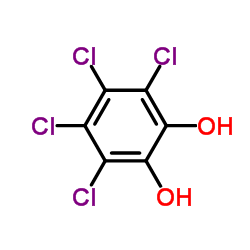
3,4,5,6-Tetrachlorobenzene-1,2-diol structure
|
Common Name | 3,4,5,6-Tetrachlorobenzene-1,2-diol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1198-55-6 | Molecular Weight | 247.891 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 309.1±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H2Cl4O2 | Melting Point | 184-186°C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 140.7±26.5 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Polyhalogenated benzo- and naphthoquinones are potent inhibitors of plant and bacterial ureases.
FEBS Lett. 555(2) , 367-70, (2003) Polyhalogenated benzo- and naphthoquinones were found to be potent inhibitors of pure ureases from Bacillus pasteurii and Canavalia ensiformis. They also inhibited ureases in whole cells of Helicobacter pylori, Klebsiella oxytoca and Proteus mirabilis. Inhibi... |
|
|
Oxidative double dehalogenation of tetrachlorocatechol by a bio-inspired CuII complex: formation of chloranilic acid.
Chemistry 14(18) , 5567-76, (2008) Copper(II) complexes of the potentially tripodal N,N,O ligand 3,3-bis(1-methylimidazol-2-yl)propionate (L1) and its conjugate acid HL1 have been synthesised and structurally and spectroscopically characterised. The reaction of equimolar amounts of ligand and ... |
|
|
Synergistic cytotoxic effect of tetrachlorocatechol and sodium azide in Escherichia coli: toxicity, metabolism, and mechanistic aspects.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 28(7) , 1380-9, (2009) Pentachlorophenol (PCP) is used in industrial and domestic applications, including as a biocide and a wood preservative. Metabolism of PCP undergoes oxidative dechlorination, forming tetrachlorocatechol (TCC) and tetrachlorohydroquinone (TCHQ). Both sodium az... |
|
|
Catechol oxidase activity of a series of new dinuclear copper(II) complexes with 3,5-DTBC and TCC as substrates: syntheses, X-ray crystal structures, spectroscopic characterization of the adducts and kinetic studies.
Inorg. Chem. 47(16) , 7083-93, (2008) A series of dinuclear copper(II) complexes has been synthesized with the aim to investigate their applicability as potential structure and function models for the active site of catechol oxidase enzyme. They have been characterized by routine physicochemical ... |
|
|
Rapid photocatalytic destruction of pentachlorophenol in F-Si-comodified TiO(2) suspensions under microwave irradiation.
J. Hazard. Mater. 161(2-3) , 1281-7, (2009) A novel photocatalysis material, F-Si-comodified TiO(2) (FST) powder, was synthesized by ultrasound-assisted hydrolysis. The prepared material was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and UV-visible absorption spect... |
|
|
Biotransformation of 2,7-dichloro- and 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by Sphingomonas wittichii RW1.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68(5) , 2584-8, (2002) Aerobic biotransformation of the diaryl ethers 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by the dibenzo-p-dioxin-utilizing strain Sphingomonas wittichii RW1, producing corresponding metabolites, was demonstrated for the first time. ... |
|
|
A novel catabolic activity of Pseudomonas veronii in biotransformation of pentachlorophenol.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 62(2-3) , 284-90, (2003) Pseudomonas veronii PH-05, a bacterial strain capable of transforming pentachlorophenol (PCP) to a metabolic intermediate, was isolated by selective enrichment of soil samples from a timber storage yard. Strain PH-05 was shown to be able to grow using PCP as ... |
|
|
Chlorocatechols substituted at positions 4 and 5 are substrates of the broad-spectrum chlorocatechol 1,2-dioxygenase of Pseudomonas chlororaphis RW71.
J. Bacteriol. 183(3) , 997-1011, (2001) The nucleotide sequence of a 10,528-bp region comprising the chlorocatechol pathway gene cluster tetRtetCDEF of the 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorobenzene via the tetrachlorocatechol-mineralizing bacterium Pseudomonas chlororaphis RW71 (T. Potrawfke, K. N. Timmis, and R.... |
|
|
Acute toxicities of pentachlorophenol, pentachloroanisole, tetrachlorohydroquinone, tetrachlorocatechol, tetrachlororesorcinol, tetrachlorodimethoxybenzenes and tetrachlorobenzenediol diacetates administered to mice. Renner G, et al.
Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 11(1) , 37-50, (1986)
|