Applied and Environmental Microbiology
2002-05-01
Biotransformation of 2,7-dichloro- and 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by Sphingomonas wittichii RW1.
Hyo-Bong Hong, Yoon-Seok Chang, In-Hyun Nam, Peter Fortnagel, Stefan Schmidt
Index: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68(5) , 2584-8, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
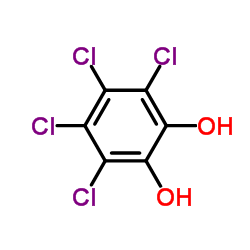
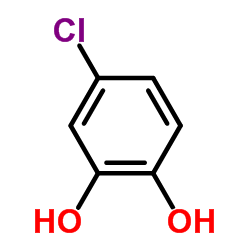
Aerobic biotransformation of the diaryl ethers 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by the dibenzo-p-dioxin-utilizing strain Sphingomonas wittichii RW1, producing corresponding metabolites, was demonstrated for the first time. Our strain transformed 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, yielding 4-chlorocatechol, and 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, producing 3,4,5,6-tetrachlorocatechol and 2-methoxy-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorophenol; all of these compounds were unequivocally identified by mass spectrometry both before and after N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)-trifluoroacetamide derivatization by comparison with authentic standards. Additional experiments showed that strain RW1 formed a second metabolite, 2-methoxy-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorophenol, from the original degradation product, 3,4,5,6-tetrachlorocatechol, by methylation of one of the two hydroxy substituents.