A novel catabolic activity of Pseudomonas veronii in biotransformation of pentachlorophenol.
I-H Nam, Y-S Chang, H-B Hong, Y-E Lee
Index: Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 62(2-3) , 284-90, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Pseudomonas veronii PH-05, a bacterial strain capable of transforming pentachlorophenol (PCP) to a metabolic intermediate, was isolated by selective enrichment of soil samples from a timber storage yard. Strain PH-05 was shown to be able to grow using PCP as the sole source of carbon and energy. GC-MS analysis showed that the metabolic intermediate was tetrachlorocatechol, which inhibited the growth of this strain. The formation of tetrachlorocatechol during biotransformation was monitored, and its inhibitory effect on growth of strain PH-05 was analyzed at a range of concentrations. The catabolic activity of the isolated strain differs from that of other PCP-degrading bacteria, which metabolize PCP through a chlorinated hydroquinone intermediate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
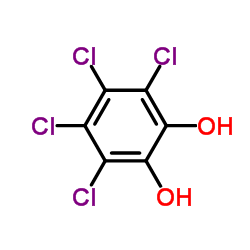 |
3,4,5,6-Tetrachlorobenzene-1,2-diol
CAS:1198-55-6 |
C6H2Cl4O2 |
|
Polyhalogenated benzo- and naphthoquinones are potent inhibi...
2003-12-04 [FEBS Lett. 555(2) , 367-70, (2003)] |
|
Oxidative double dehalogenation of tetrachlorocatechol by a ...
2008-01-01 [Chemistry 14(18) , 5567-76, (2008)] |
|
Synergistic cytotoxic effect of tetrachlorocatechol and sodi...
2009-07-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 28(7) , 1380-9, (2009)] |
|
Catechol oxidase activity of a series of new dinuclear coppe...
2008-08-18 [Inorg. Chem. 47(16) , 7083-93, (2008)] |
|
Rapid photocatalytic destruction of pentachlorophenol in F-S...
2009-01-30 [J. Hazard. Mater. 161(2-3) , 1281-7, (2009)] |