Juglone
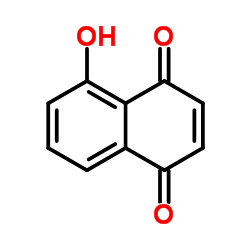
Juglone structure
|
Common Name | Juglone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 481-39-0 | Molecular Weight | 174.153 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 385.8±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H6O3 | Melting Point | 161-163 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 201.3±24.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Redox effects and cytotoxic profiles of MJ25 and auranofin towards malignant melanoma cells.
Oncotarget 6 , 16488-506, (2015) Malignant melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. Although recent progress in treatment has been achieved, lack of response, drug resistance and relapse remain major problems. The tumor suppressor p53 is rarely mutated in melanoma, yet it is inact... |
|
|
Chromatographic evaluation and QSAR optimization for benzoic acid analogues against carbonic anhydrase III.
J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 30 , 420-9, (2015) An HPLC-size exclusion method was developed as an assay method to evaluate the binding of tested compounds with carbonic anhydrase III (CAIII) enzyme. Inhibition of CAIII by a group of benzoic acid analogues was characterized by vacancy (negative) peak intens... |
|
|
Determination of the Juglone Content of Juglans regia Leaves by GC/MS.
Nat. Prod. Commun. 10 , 1239-42, (2015) The constituents of walnut (Juglans regia L.) leaves are represented by tannins, phenolics, and naphthoquinones, the characteristic compound being juglone. The content of juglone in the methanolic extract of the leaves determined by the GC/MS method was 9.9 ±... |
|
|
Enhanced eryptosis following juglone exposure.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 116 , 460-7, (2015) Juglone, a quinone isolated from Juglans mandshurica Maxim, has previously been shown to be effective against malignancy. The effect is at least partially due to stimulation of suicidal death or apoptosis of tumour cells. On the other hand, juglone has been s... |
|
|
A chemical screening approach reveals that indole fluorescence is quenched by pre-fibrillar but not fibrillar amyloid-beta.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 4952-7, (2009) Aggregated amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide is implicated in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. In vitro and in vivo, these aggregates are found in a variety of morphologies, including globular oligomers and linear fibrils, which possess distinct biological ac... |
|
|
Bioactivities of simplified adociaquinone B and naphthoquinone derivatives against Cdc25B, MKP-1, and MKP-3 phosphatases.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 2276-81, (2009) Some simplified adociaquinone B analogs and a series of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives were synthesized and tested against the three enzymes Cdc25B, MKP-1, and MKP-3. Cdc25B and MKP-1 in particular are enzymes overexpressed in human cancer cells, and they rep... |
|
|
Inhibitory effect of novel 5-O-acyl juglones on mammalian DNA polymerase activity, cancer cell growth and inflammatory response.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 5803-5812, (2011) We previously found that vitamin K(3) (menadione, 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) inhibits the activity of human mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ (pol γ). In this study, we focused on juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone), which is a 1,4-naphthoquinone derivative... |
|
|
Mitochondrial and cytoplasmic ROS have opposing effects on lifespan.
PLoS Genet. 11(2) , e1004972, (2015) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive, oxygen-containing molecules that can cause molecular damage within the cell. While the accumulation of ROS-mediated damage is widely believed to be one of the main causes of aging, ROS also act in signaling p... |
|
|
Yellow Pigment Aurovertins Mediate Interactions between the Pathogenic Fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia and Its Nematode Host.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 6577-87, (2015) Nematophagous fungi are globally distributed soil fungi and well-known natural predators of soil-dwelling nematodes. Pochonia chlamydosporia can be found in diverse nematode-suppressive soils as a parasite of nematode eggs and is one of the most studied poten... |
|
|
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is the anticancer target for a novel series of potent naphthoquinone-based inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 1706-18, (2008) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is emerging as an important new therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer, chronic viral infections, and other diseases characterized by pathological immune suppression. While small molecule inhibitors of IDO exist, ther... |