Methyl Vinyl sulphone
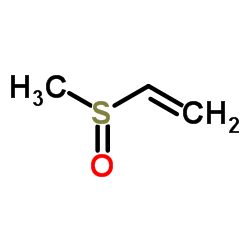
Methyl Vinyl sulphone structure
|
Common Name | Methyl Vinyl sulphone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3680-02-2 | Molecular Weight | 90.144 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 201.2±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6OS | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 75.5±19.8 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Usp5 links suppression of p53 and FAS levels in melanoma to the BRAF pathway.
Oncotarget 5(14) , 5559-69, (2014) Usp5 is a deubiquitinase (DUB) previously shown to regulate unanchored poly-ubiquitin (Ub) chains, p53 transcriptional activity and double-strand DNA repair. In BRAF mutant melanoma cells, Usp5 activity was suppressed by BRAF inhibitor (vemurafenib) in sensit... |
|
|
Protein reactions with methyl and ethyl vinyl sulfones.
J. Protein Chem. 7(1) , 49-54, (1988) Disulfide bonds of bovine serum albumin and wool were reduced by n-tributylphosphine to sulfhydryl groups that were then modified by methyl or ethyl vinyl sulfone in a nucleophilic addition reaction to S-(beta-ethylsulfonylmethyl)-L-cysteine and S(beta-ethyls... |
|
|
Trypanocidal activities of trileucine methyl vinyl sulfone proteasome inhibitors.
Parasitol. Res. 95(1) , 73-6, (2005) Previous studies have shown that proteasome inhibitors are novel agents for chemotherapy of human African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness. In this study, five peptide trileucine methyl vinyl sulfones with different N-terminal substituents were tested for... |
|
|
Synthesis , 3495, (2006)
|
|
|
Structural components in methyl vinyl sulfone modified cotton cellulose. Rowland SP, et al.
Can. J. Chem. 44(9) , 1051-58, (1966)
|
|
|
Pseudouridine detection improvement by derivatization with methyl vinyl sulfone and capillary HPLC-mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 825(2) , 233-8, (2005) A method is presented for improved detection of pseudouridine in nucleoside mixtures based on the specific derivatization with methyl vinyl sulfone followed by analysis by capillary HPLC-mass spectrometry. Reaction conditions were optimized in order to obtain... |
|
|
Genotoxicity in mouse lymphoma cells of chemicals capable of Michael addition.
Mutagenesis 6(6) , 519-25, (1991) Over the past several years, we have been evaluating the mutagenicity and clastogenicity of compounds capable of Michael-type reactions. These compounds, including acrylamide, several acrylate and methacrylate esters, vinyl sulfones, and phorone, have been ev... |
|
|
Methyl vinyl sulphone: a new class of Michael-type genotoxin.
Mutat. Res. 245(3) , 191-9, (1990) Methyl vinyl sulphone (MVS) is a labile, Michael-reactive chemical, similar in structure to acrylamide (AA). Given that acrylamide is a reference mammalian mutagen and a rodent carcinogen, studies were undertaken to evaluate the potential genotoxicity of MVS.... |
|
|
Mouse dominant lethal and bone marrow micronucleus studies on methyl vinyl sulfone and divinyl sulfone.
Mutat. Res. 250(1-2) , 431-7, (1991) Methyl vinyl sulfone and divinyl sulfone were tested for the induction of dominant lethal mutations and micronucleated bone-marrow erythrocytes in male mice. These chemicals were chosen for study because of their similarities in structure and chemical reactiv... |
|
|
Induction of NAD(P)H:quinone reductase in human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Carcinogenesis 12(12) , 2393-6, (1991) The induction of quinone reductase [QR; NAD(P)H:(quinone acceptor) oxidoreductase; EC 1.6.99.2] in cultured cells and animal tissues of rodents has provided useful information on mechanisms of protection against carcinogens. We have developed a simple and eff... |