UNII:H1547KG7UZ
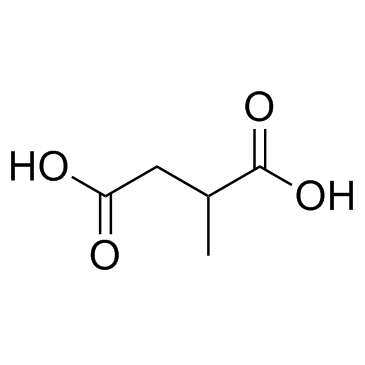
UNII:H1547KG7UZ structure
|
Common Name | UNII:H1547KG7UZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 498-21-5 | Molecular Weight | 132.115 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 236.5±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O4 | Melting Point | 110-115 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 111.1±16.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population.
Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994) Organic acid concentrations were quantified by gas chromatography and the individual acids identified by mass spectrometry in urine specimens from a healthy Turkish pediatric population of ages 2 days to 16 years, subdivided into five age groups. We quantifie... |
|
|
SPE-NMR metabolite sub-profiling of urine.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 404(8) , 2349-61, (2012) NMR-based metabolite profiling of urine is a fast and reproducible method for detection of numerous metabolites with diverse chemical properties. However, signal overlap in the (1)H NMR profiles of human urine may hamper quantification and identification of m... |
|
|
Concentrations of riboflavin and related organic acids in children with protein-energy malnutrition.
Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71(4) , 978-86, (2000) Riboflavin, flavin mononucleotide (FMN), and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) concentrations have been little studied in cases of malnutrition.Our objective was to investigate the effects of malnutrition on riboflavin status and riboflavin's relation with th... |
|
|
Intrinsic biodegradation potential of aromatic hydrocarbons in an alluvial aquifer--potentials and limits of signature metabolite analysis and two stable isotope-based techniques.
Water Res. 45(15) , 4459-69, (2011) Three independent techniques were used to assess the biodegradation of monoaromatic hydrocarbons and low-molecular weight polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the alluvial aquifer at the site of a former cokery (Flémalle, Belgium). Firstly, a stable carbon isotope-ba... |
|
|
2,6-Dimethyloctanedioic acid--a metabolite of phytanic acid in Refsum's disease.
Clin. Chem. 29(3) , 434-7, (1983) The urine of two patients with Refsum's disease consistently contained 2,6-dimethyloctanedioic acid, a compound not normally found in human urine. In addition, their urines contained increased concentrations of 3-methylhexanedioic acid. These two compounds ma... |
|
|
Metabolism of phytanic acid and 3-methyl-adipic acid excretion in patients with adult Refsum disease.
J. Lipid Res. 44(8) , 1481-8, (2003) Adult Refsum disease (ARD) is associated with defective alpha-oxidation of phytanic acid (PA). omega-Oxidation of PA to 3-methyl-adipic acid (3-MAA) occurs although its clinical significance is unclear. In a 40 day study of a new ARD patient, where the plasma... |
|
|
Infantile Refsum's disease: biochemical findings suggesting multiple peroxisomal dysfunction.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 9(2) , 169-74, (1986) Infantile Refsum's disease was diagnosed in three male patients, presenting with facial dysmorphia, retinitis pigmentosa, neurosensory hearing loss, hepatomegaly, osteopenia and delayed growth and psychomotor development. An elevated plasma phytanic acid conc... |
|
|
Antimalarial halorosellinic acid from the marine fungus Halorosellinia oceanica.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11(15) , 1965-9, (2001) Three known compounds, 2-hexylidene-3-methylsuccinic acid (1), cytochalasin Q (2), and 5-carboxymellein (3), together with two new derivatives, 2-hexylidene-3-methylsuccinic acid 4-methyl ester (4) and an ophiobolane sesterterpene named halorosellinic acid (5... |
|
|
A constitutive nitric oxide synthase modulates insulin secretion in the INS-1 cell line.
Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 183(1-2) , 41-8, (2001) We provide immunocytochemical evidence that the neuronal isoform of constitutive NO synthase (cNOS) is expressed in the rat insulinoma cell line INS-1. Furthermore, using N omega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), a pharmacological inhibitor of cNOS acti... |
|
|
Ethylmalonic encephalopathy: further clinical and neuroradiological characterization.
J. Neurol. 249(10) , 1446-50, (2002) Ethylmalonic encephalopathy (EE) is a rare metabolic disorder with an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance that is clinically characterized by neuromotor delay, hyperlactic acidemia, recurrent petechiae, orthostatic acrocyanosis, and chronic diarrhea. Incr... |