| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
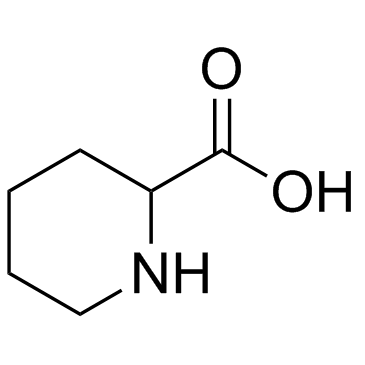 |
Pipecolinic acid
CAS:535-75-1 |
|
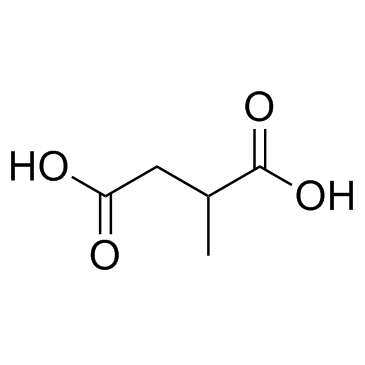 |
UNII:H1547KG7UZ
CAS:498-21-5 |
|
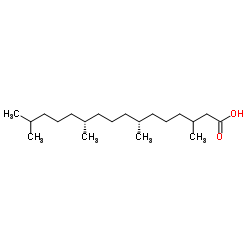 |
Phytanic acid
CAS:14721-66-5 |
|
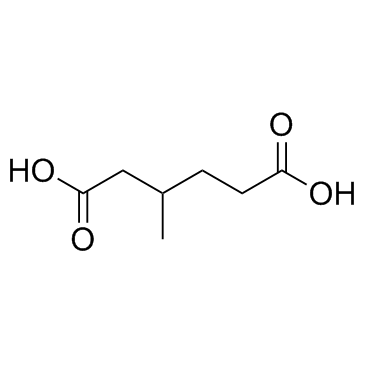 |
3-Methyladipic acid
CAS:3058-01-3 |