pralidoxime
Modify Date: 2025-09-18 18:00:16
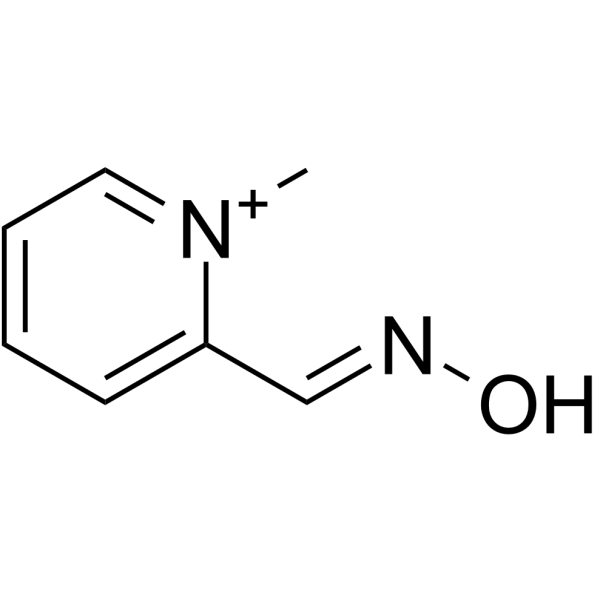
pralidoxime structure
|
Common Name | pralidoxime | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6735-59-7 | Molecular Weight | 137.15900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9N2O+ | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of pralidoximePralidoxime is a potent reactivator of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Pralidoxime reactivates nerve agent-inhibited AChE via direct nucleophilic attack by the oxime moiety on the phosphorus center of the bound nerve agent. Pralidoxime is an antidote for organophosphate poisoning[1][2]. |
| Name | pralidoxime |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pralidoxime is a potent reactivator of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Pralidoxime reactivates nerve agent-inhibited AChE via direct nucleophilic attack by the oxime moiety on the phosphorus center of the bound nerve agent. Pralidoxime is an antidote for organophosphate poisoning[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Acetylcholinesterase |
| In Vivo | Pralidoxime (10-150 mg/kg; intramuscular administration, once) reverses paraoxon-induced respiratory toxicity in mice[3]. Animal Model: F1B6D2 mice (male, administered subcutaneously diethylparaoxon)[3] Dosage: 10, 50, 100, and 150 mg/kg Administration: Intramuscular administration, once Result: Induced a partial, albeit complete, reversal of respiratory toxicity at 50 mg/kg, and completely reversed diethylparaoxon-induced respiratory toxicity in mice at 150 mg/kg. |
| References |
[2]. Eyer P, Buckley N. Pralidoxime for organophosphate poisoning. Lancet. 2006;368(9553):2110‐2111. |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9N2O+ |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 137.15900 |
| Exact Mass | 137.07100 |
| PSA | 36.47000 |
| LogP | 0.31920 |
| Conthrathion |
| 2-(hydroxyimino-methyl)-1-methyl-pyridinium |
| PRALIDOXIME |
| N-Methyl-2-pyridyl-aldoxim-hydroxid |
| 2-PAM |
| 2-(Hydroxyiminomethyl)-1-methylpyridinium |
| 2-(hydroximinomethyl)-1-methylpyridinium cation |
| (2-Hydroxyimino-methyl)-1-methyl-pyridinium |