2-Pyridinealdoxime methochloride
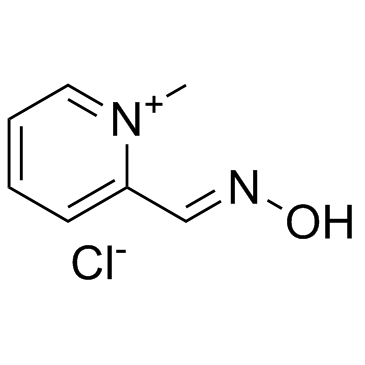
2-Pyridinealdoxime methochloride structure
|
Common Name | 2-Pyridinealdoxime methochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51-15-0 | Molecular Weight | 172.612 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 189.7ºC at760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9ClN2O | Melting Point | 215-225 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 68.5ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2-Pyridinealdoxime methochloridePralidoxime chloride is a useful agent in the treatment of organophosphate poisoning. Pralidoxime binds to organophosphate-inactivated acetylcholinesterase, used to combat poisoning by organophosphates or acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (nerve agents) in conjunction with atropine and diazepam. |
| Name | pralidoxime chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pralidoxime chloride is a useful agent in the treatment of organophosphate poisoning. Pralidoxime binds to organophosphate-inactivated acetylcholinesterase, used to combat poisoning by organophosphates or acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (nerve agents) in conjunction with atropine and diazepam. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Boiling Point | 189.7ºC at760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 215-225 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9ClN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 172.612 |
| Flash Point | 68.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 172.040344 |
| PSA | 36.47000 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Water Solubility | 65.5 g/100 mL (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36-S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UU4200000 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|
~90% 
2-Pyridinealdox... CAS#:51-15-0 |
| Literature: Unnisa, Lateef; Sumakanth; Rao, B. Leelamaheswara; Divi, Murali Krishnaprasad; Rao, Mysore Aswathanarayana Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section B Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2014 , vol. 53, # 4 p. 431 - 435 |
|
~89% 
2-Pyridinealdox... CAS#:51-15-0 |
| Literature: Unnisa, Lateef; Sumakanth; Rao, B. Leelamaheswara; Divi, Murali Krishnaprasad; Rao, Mysore Aswathanarayana Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section B Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2014 , vol. 53, # 4 p. 431 - 435 |
|
~% 
2-Pyridinealdox... CAS#:51-15-0 |
| Literature: Unnisa, Lateef; Sumakanth; Rao, B. Leelamaheswara; Divi, Murali Krishnaprasad; Rao, Mysore Aswathanarayana Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section B Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2014 , vol. 53, # 4 p. 431 - 435 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Development and validation of a FIA/UV-vis method for pK(a) determination of oxime based acetylcholinesterase reactivators.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 117 , 240-6, (2015) Acetylcholinesterase reactivators (oximes) are compounds used for antidotal treatment in case of organophosphorus poisoning. The dissociation constants (pK(a1)) of ten standard or promising acetylchol... |
|
|
An in vivo zebrafish screen identifies organophosphate antidotes with diverse mechanisms of action.
J. Biomol. Screen. 18(1) , 108-15, (2013) Organophosphates are a class of highly toxic chemicals that includes many pesticides and chemical weapons. Exposure to organophosphates, either through accidents or acts of terrorism, poses a signific... |
|
|
Chlorpyrifos is associated with slower serum cholinesterase recovery in acute organophosphate-poisoned patients.
Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 51(5) , 402-8, (2013) Organophosphate poisoning (OPP) accounts for 200,000 deaths annually in developing countries. Serum cholinesterase (SChE) is of diagnostic value in patients with OPP and is checked repeatedly during t... |
| Pyraloximi Methchlordum |
| protopamchloride |
| 1-methyl-2-pyridine aldoxyme chloride |
| 2-[(E)-(Hydroxyimino)methyl]-1-methylpyridinium chloride |
| 2-Pyridine aldoxime methyl chloride |
| pralidoxime |
| EINECS 200-080-9 |
| pyridinium, 2-[(hydroxyimino)methyl]-1-methyl-, chloride (1:1) |
| 2-Pyridinealdoxime methochloride |
| Pralidoxome Chloride |
| Pralidoxime Chloride |
| pyridinium, 2-[(E)-(hydroxyimino)methyl]-1-methyl-, chloride |
| 2-PAM CHLORIDE |
| 2-[hydroxyimino ethyl]-1-methylpyridinium chloride |
| MFCD00011981 |
| Protopam |
| Pyridine-2-aldoxiMe Meth |
| PRALIDOXIMECHLORIDE,USP |
| 2-[(Hydroxyimino)methyl]-1-methylpyridinium chloride |
| Pyridinium, 2-[(E)-(hydroxyimino)methyl]-1-methyl-, chloride (1:1) |
| 2-PAM-Cl |
| 1-MethylpyridiniuM-2-aldoxiMe Chloride |
| PAM CHLORIDE |