Asoxime dichloride
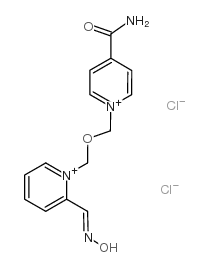
Asoxime dichloride structure
|
Common Name | Asoxime dichloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34433-31-3 | Molecular Weight | 359.20800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H16Cl2N4O3 | Melting Point | 145-147ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Asoxime dichlorideAsoxime dichloride (HI-6) is an antagonist to acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) including the nicotinic receptor, α7 nAChR. Asoxime dichloride involves in modulating immunity response. Asoxime dichloride (HI-6) can be used as an antigen and improves vaccination efficacy in the nervous system[1]. |
| Name | asoxime chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Asoxime dichloride (HI-6) is an antagonist to acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) including the nicotinic receptor, α7 nAChR. Asoxime dichloride involves in modulating immunity response. Asoxime dichloride (HI-6) can be used as an antigen and improves vaccination efficacy in the nervous system[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: acetylcholine receptors (AChRs)[1] |
| In Vivo | Asoxime dichloride (intramuscular injection into the rear limb; 2% and 0.2% of median lethal dose 15.6 and 1.56 mg/kg; 21 or 65 days) significantly improved vaccination efficacy as a dose-dependent manner when KLH is 1 mg/kg. A combination of HI-6 and keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) produces a vaccination of almost the same efficacy as that for Freund's complete adjuvant[1]. Animal Model: Balb/c mice[1] Dosage: 2% and 0.2% of median lethal dose 15.6 and 1.56mg/kg Administration: Intramuscular injection into the rear limb Result: Improved vaccination efficacy at the level of immunity regulation by the nervous system. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 145-147ºC |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H16Cl2N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 359.20800 |
| Exact Mass | 358.06000 |
| PSA | 92.67000 |
| Storage condition | 20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
Effect of reversible ligands on oxime-induced reactivation of sarin- and cyclosarin-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase.
Toxicol. Lett. 232(3) , 557-65, (2015) Poisoning by organophosphorus compounds (OP) used as pesticides and nerve agents is due to irreversible inhibition of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Oximes have been widely recognized for the... |
|
|
The effect of oxime reactivators on muscarinic receptors: functional and binding examinations.
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 31(3) , 364-70, (2011) The antidotal treatment of organophosphorus poisoning is still a problematic issue since no versatile antidote has been developed yet. In our study, we focused on an interesting property, which does n... |
|
|
Syntheses and in vitro evaluations of uncharged reactivators for human acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 203(1) , 81-4, (2013) Organophosphorus nerve agents (OPNAs) are highly toxic compounds that represent a threat to both military and civilian populations. They cause an irreversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE)... |
| Pralidoxime |
| hi-6dichloride |
| hj6 |
| hi6 |
| HI 6 Chloride |
 CAS#:142-08-5
CAS#:142-08-5 CAS#:100-70-9
CAS#:100-70-9 CAS#:873-69-8
CAS#:873-69-8 CAS#:55-22-1
CAS#:55-22-1 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0 CAS#:1453-82-3
CAS#:1453-82-3 CAS#:1452-77-3
CAS#:1452-77-3