5-hydroxymethylfurfural
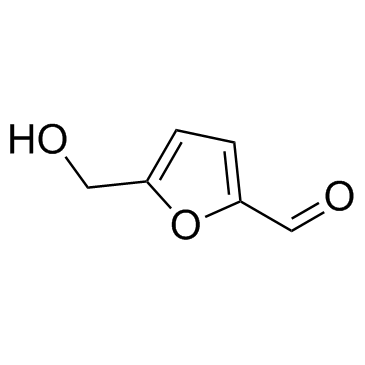
5-hydroxymethylfurfural structure
|
Common Name | 5-hydroxymethylfurfural | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67-47-0 | Molecular Weight | 126.110 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 291.5±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6O3 | Melting Point | 28-34 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 79.4±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural5-(Hydroxymethyl)furan-2-carbaldehyde, derived from lignocellulosic biomass, inhibits yeast growth and fermentation as stressors. |
| Name | 5-hydroxymethylfurfural |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furan-2-carbaldehyde, derived from lignocellulosic biomass, inhibits yeast growth and fermentation as stressors. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Yeast[1]. |
| In Vitro | It is found that furfural and HMF cause the attenuation of bulk translation activity and the assembly of cytoplasmic mRNP granules in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Notably, a combination of furfural and HMF induce the remarkable repression of translation initiation and SG formation. Furfural and HMF can induce the formation of cytoplasmic mRNP granules, HMF also causes a gradual reduction in the polysome fraction and a concomitant increase in the 80S monosome fraction[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 291.5±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 28-34 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 126.110 |
| Flash Point | 79.4±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 126.031693 |
| PSA | 50.44000 |
| LogP | -0.45 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.563 |
| InChIKey | NOEGNKMFWQHSLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=Cc1ccc(CO)o1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Light Sensitive, Very Hygroscopic |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P304 + P340 + P312-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | LT7031100 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| HS Code | 2932190090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2932190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932190090 other compounds containing an unfused furan ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:20.0% |
|
Detoxification of biomass hydrolysates with nucleophilic amino acids enhances alcoholic fermentation.
Bioresour. Technol. 186 , 106-13, (2015) Carbonyl compounds generated in biomass pretreatment hinder the biochemical conversion of biomass hydrolysates to biofuels. A novel approach of detoxifying hydrolysates with amino acids for ethanol pr... |
|
|
Structural features of dilute acid, steam exploded, and alkali pretreated mustard stalk and their impact on enzymatic hydrolysis.
Carbohydr. Polym. 124 , 265-73, (2015) To overcome the recalcitrant nature of biomass several pretreatment methodologies have been explored to make it amenable to enzymatic hydrolysis. These methodologies alter cell wall structure primaril... |
|
|
Comparison of different process strategies for bioethanol production from Eucheuma cottonii: An economic study.
Bioresour. Technol. 199 , 336-46, (2015) The aim of this work was to evaluate the efficacy of red macroalgae Eucheuma cottonii (EC) as feedstock for third-generation bioethanol production. Dowex (TM) Dr-G8 was explored as a potential solid c... |
| HMF |
| EINECS 200-654-9 |
| 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furan-2-carboxaldehyde |
| T5OJ BVH E1Q |
| 5-(Hydroxymethyl)-2-furancarboxaldehyde |
| 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furan-2-carbaldehyde |
| Aes-103 |
| 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furfural |
| 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural |
| 2-Furancarboxaldehyde, 5-(hydroxymethyl)- |
| MFCD00003234 |
| 2-furaldehyde, 5-(hydroxymethyl)- |
 CAS#:87-79-6
CAS#:87-79-6 CAS#:470-23-5
CAS#:470-23-5 CAS#:50-99-7
CAS#:50-99-7 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1 CAS#:57-48-7
CAS#:57-48-7 CAS#:57-50-1
CAS#:57-50-1 CAS#:2280-44-6
CAS#:2280-44-6 CAS#:6347-01-9
CAS#:6347-01-9 CAS#:10489-79-9
CAS#:10489-79-9 CAS#:110339-34-9
CAS#:110339-34-9 CAS#:10299-30-6
CAS#:10299-30-6 CAS#:104-80-3
CAS#:104-80-3 CAS#:106-69-4
CAS#:106-69-4 CAS#:65313-46-4
CAS#:65313-46-4 CAS#:64-18-6
CAS#:64-18-6 CAS#:328-50-7
CAS#:328-50-7 CAS#:110-15-6
CAS#:110-15-6 CAS#:4282-32-0
CAS#:4282-32-0
