Propargyl-PEG1-acid
Modify Date: 2025-08-22 19:54:37
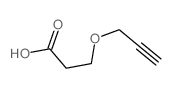
Propargyl-PEG1-acid structure
|
Common Name | Propargyl-PEG1-acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 55683-37-9 | Molecular Weight | 128.12600 | |
| Density | 1.14g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 265.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H8O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 113.9ºC | |
Use of Propargyl-PEG1-acidPropargyl-PEG1-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker can be used in the synthesis of BTK-CRBN PROTACs Ibrutinib(HY-10997)-based PROTAC 4 and PROTAC 5. PROTAC 5 causes the degradation of BTK and induces the degradation of CSK, LYN, and LAT2 at 10 μM[1]. |
| Name | 3-prop-2-ynoxypropanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Propargyl-PEG1-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker can be used in the synthesis of BTK-CRBN PROTACs Ibrutinib(HY-10997)-based PROTAC 4 and PROTAC 5. PROTAC 5 causes the degradation of BTK and induces the degradation of CSK, LYN, and LAT2 at 10 μM[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PEGs |
| In Vitro | BTK-CRBN PROTACs act as stoichiometric degraders, resulting in degradation of BTK protein. Degradation of BTK is a result of cereblon E3 ligases family recruitment[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.14g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 265.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C6H8O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 128.12600 |
| Flash Point | 113.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 128.04700 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 0.11090 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.463 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Propargyl-PEG1-acid |


