H-D-Asp-OH
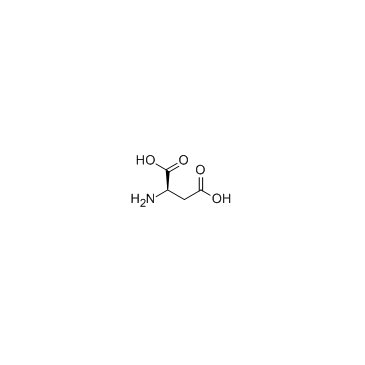
H-D-Asp-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-D-Asp-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1783-96-6 | Molecular Weight | 133.103 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 264.1±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 | Melting Point | 300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 113.5±24.6 °C | |
Use of H-D-Asp-OH(-)-Aspartic acid is an endogenous NMDA receptor agonist. |
| Name | D-aspartic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (-)-Aspartic acid is an endogenous NMDA receptor agonist. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 264.1±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 300ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 133.103 |
| Flash Point | 113.5±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 133.037506 |
| PSA | 100.62000 |
| LogP | -0.67 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.531 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CI9097500 |
| HS Code | 29224995 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Coupling substrate and ion binding to extracellular gate of a sodium-dependent aspartate transporter.
Nature 445 , 387-93, (2007) Secondary transporters are integral membrane proteins that catalyse the movement of substrate molecules across the lipid bilayer by coupling substrate transport to one or more ion gradients, thereby p... |
|
|
Oral administration of D-aspartate, but not L-aspartate, depresses rectal temperature and alters plasma metabolites in chicks.
Life Sci. 109(1) , 65-71, (2014) L-Aspartate (L-Asp) and D-aspartate (D-Asp) are physiologically important amino acids in mammals and birds. However, the functions of these amino acids have not yet been fully understood. In this stud... |
|
|
Okibacterium endophyticum sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from roots of Salsola affinis C. A. Mey.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107(3) , 835-43, (2015) A white bacterial strain, designated EGI 650022(T), was isolated from the roots of Salsola affinis C. A. Mey, collected from Urumqi City, Xinjiang, north-western China. The strain was found to be aero... |
| δ-aspartic acid |
| D(-)-Aspartic acid |
| d-Asp |
| QVYZ1VQ &&D or R Form |
| (-)-Aspartic acid |
| (2R)-2-Aminosuccinic acid |
| Aspartic acid,D |
| D-Aspartate |
| MFCD00063081 |
| (2R)-2-aminobutanedioic acid |
| hydrogen D-aspartate |
| (R)-2-Aminosuccinic acid |
| (R)-Aminosuccinic Acid |
| D-Asparaginic Acid |
| (R)-(−)-Aminosuccinic acid |
| D-(-)-Aspartic acid |
| (R)-(−)-Aminosuccinic acid,(R)-2-Aminosuccinic acid |
| Acide (2R)-2-aminosuccinique |
| aspartic acid D-form |
| D-Asparticacid |
| EINECS 217-234-6 |
| Aspartic acid, D- |
| D-Aspartic acid |
| H-D-Asp-OH |
| L-Ornithine L-Aspartate Impurity 1 |
 CAS#:328-42-7
CAS#:328-42-7 CAS#:338-69-2
CAS#:338-69-2 CAS#:2058-58-4
CAS#:2058-58-4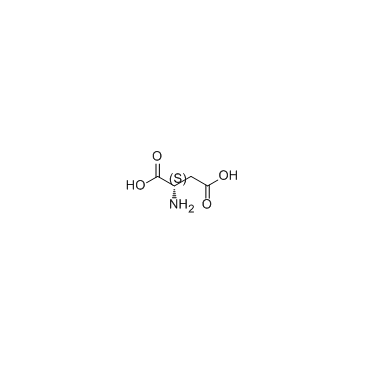 CAS#:56-84-8
CAS#:56-84-8![2-[(2-chloroacetyl)amino]butanedioic acid Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/493/67036-33-3.png) CAS#:67036-33-3
CAS#:67036-33-3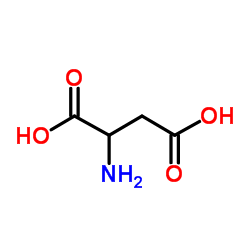 CAS#:617-45-8
CAS#:617-45-8 CAS#:923-06-8
CAS#:923-06-8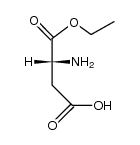 CAS#:565461-05-4
CAS#:565461-05-4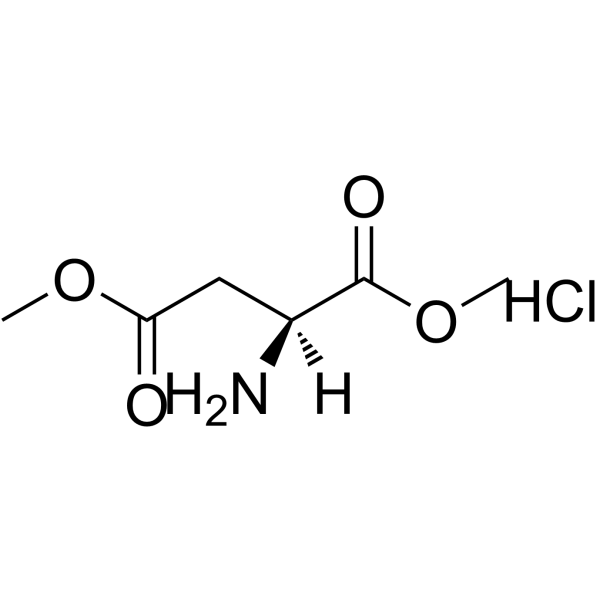 CAS#:32213-95-9
CAS#:32213-95-9 CAS#:4079-64-5
CAS#:4079-64-5 CAS#:14358-33-9
CAS#:14358-33-9 CAS#:3972-40-5
CAS#:3972-40-5 CAS#:78663-07-7
CAS#:78663-07-7 CAS#:6384-92-5
CAS#:6384-92-5 CAS#:636-61-3
CAS#:636-61-3 CAS#:128574-89-0
CAS#:128574-89-0 CAS#:118399-28-3
CAS#:118399-28-3
