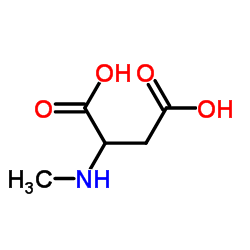
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
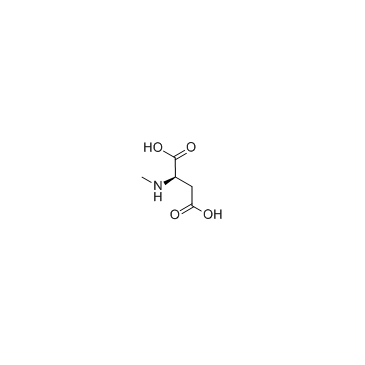
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid structure
|
Common Name | N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6384-92-5 | Molecular Weight | 147.129 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 258.2±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4 | Melting Point | 187-192 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 110.0±24.6 °C | |
Use of N-Methyl-D-aspartic acidNMDA is a specific agonist for NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. |
| Name | N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | NMDA is a specific agonist for NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | NMDA exerts a significant augmentation of the adrenal binding independently of the incubation temperature in a concentration-dependent manner[2]. |
| In Vivo | NMDA (0.2 nM) shows significant effects on MF, IF, IL, and EL, respectively, decreasing the mount and intromission frequencies, and shortening the intromission and ejaculation latencies. NMDA and AP-5 significantly, respectively, facilitates and inhibits the ejaculatory behavior during the copulation testing 30 min. Bilateral microinjection of NMDA into PVN significantly increases the baseline LSNA, the peaking increment of LSNA occurred within 5 min from the time of NMDA microinjected into PVN[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Adrenal membranous homogenate suspensions are incubated with 10 nM [3H]Glu in 500/zl 50 mM Tris-acetate buffer (pH 7.4) at 2°C or 30°C in the presence and absence of various compounds. Incubation is terminated by the addition of 3 mL ice-cold buffer and subsequent filtration through a Whatman GF/B glass filter under a constant vacuum of 15 mm Hg. After washing the filter 4 times with 3 mL icecold buffer, the radioactivity trapped on the filter is measured by a liquid scintillation spectrometer using 5 mL modified Triton-toluene scintillant at a counting efficiency of 40-42%. The radioactivity found in the presence of 1 mM non-radioactive Glu is subtracted from each experimental value to obtain the specific binding of [3H]GIu in accordance with the y-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding assay system. The kinetic parameters of [3H]GIu binding, Kd and Bma x, are calculated by Scatchard analysis of the specific binding using a personal computer with a programme for non-linear regression analysis developed in our own laboratory. |
| Animal Admin | Thirty male rats are paired with different receptive females for a total of three times (once every 3 days) a week prior to the experiment, only the males that ejaculated at least three times during this period are included. After selecting the male rats with normal ejaculatory ability. Saline (100 nL), NMDA (0.20 nmol in 100 nL saline), and AP-5 (10.0 nmol in 100 nL saline) are adminitration into the bilateral PVN of each male rat in random order. After 5 min, the behavioral testing is performed and recorded as described above. Copulatory behaviors occur once a week and the entire experiment lasted 4 weeks. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 258.2±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 187-192 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 147.129 |
| Flash Point | 110.0±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 147.053162 |
| PSA | 86.63000 |
| LogP | -0.44 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.494 |
| InChIKey | HOKKHZGPKSLGJE-GSVOUGTGSA-N |
| SMILES | CNC(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CI9457000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|
~% 
N-Methyl-D-aspa... CAS#:6384-92-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 45, p. 2005 - 2011 |
|
~% 
N-Methyl-D-aspa... CAS#:6384-92-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 45, p. 2005 - 2011 |
|
~% 
N-Methyl-D-aspa... CAS#:6384-92-5 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 45, p. 2005 - 2011 |
|
~% 
N-Methyl-D-aspa... CAS#:6384-92-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, , vol. 5, p. 1187 - 1199 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 75, # 23 p. 8012 - 8023 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 75, # 23 p. 8012 - 8023 |
|
~% 
N-Methyl-D-aspa... CAS#:6384-92-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, , vol. 5, p. 1187 - 1199 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Long-term application of glycine transporter inhibitors acts antineuropathic and modulates spinal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR-1 expression in rats.
Anesthesiology 121(1) , 160-9, (2014) Dysfunction of spinal glycinergic neurotransmission is a major pathogenetic factor in neuropathic pain. The synaptic glycine concentration is controlled by the two glycine transporters (GlyT) 1 and 2.... |
|
|
Glutamatergic receptor dysfunction in spinal cord contributes to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in heart failure.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 308(5) , H447-55, (2015) Excitatory amino acids (e.g., glutamate) released by contraction-activated skeletal muscle afferents into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord initiate the central component of the exercise pressor refl... |
|
|
Cysteine substitution of transmembrane domain amino acids alters the ethanol inhibition of GluN1/GluN2A N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 353(1) , 91-101, (2015) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are inhibited by behaviorally relevant concentrations of ethanol, and residues within transmembrane (TM) domains of NMDARs, including TM3 GluN1 phenylalanine 63... |
| N-Methylaspartic acid |
| DL-Aspartic acid, N-methyl- |
| N-Methyl-DL-Aspartic acid |
| EINECS 227-012-0 |
| DL-2-METHYLAMINOSUCCINIC ACID |
| D-Aspartic acid, N-methyl- |
| Aspartic acid, N-methyl- |
| N-Me-D-Asp-OH |
| (2R)-2-(methylamino)butanedioic acid |
| UNII:EU52DFC4WJ |
| NMDA |
| N-Methyl--aspartic acid |
| MFCD06795789 |
| N-Methyl aspartic acid |
| N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid |