N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
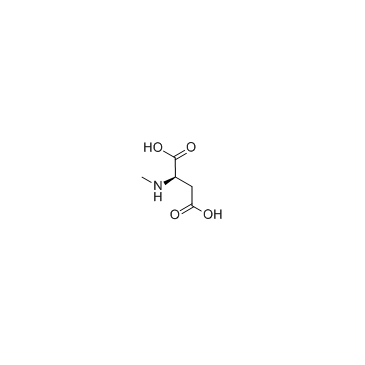
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid structure
|
Common Name | N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6384-92-5 | Molecular Weight | 147.129 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 258.2±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4 | Melting Point | 187-192 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 110.0±24.6 °C | |
|
Long-term application of glycine transporter inhibitors acts antineuropathic and modulates spinal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR-1 expression in rats.
Anesthesiology 121(1) , 160-9, (2014) Dysfunction of spinal glycinergic neurotransmission is a major pathogenetic factor in neuropathic pain. The synaptic glycine concentration is controlled by the two glycine transporters (GlyT) 1 and 2. GlyT inhibitors act antinociceptive in various animal pain... |
|
|
Glutamatergic receptor dysfunction in spinal cord contributes to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in heart failure.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 308(5) , H447-55, (2015) Excitatory amino acids (e.g., glutamate) released by contraction-activated skeletal muscle afferents into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord initiate the central component of the exercise pressor reflex (EPR) in physiological conditions. However, the role of ... |
|
|
Cysteine substitution of transmembrane domain amino acids alters the ethanol inhibition of GluN1/GluN2A N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 353(1) , 91-101, (2015) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are inhibited by behaviorally relevant concentrations of ethanol, and residues within transmembrane (TM) domains of NMDARs, including TM3 GluN1 phenylalanine 639 (F639), regulate this sensitivity. In the present study, ... |
|
|
Sigma-1 receptor deficiency reduces MPTP-induced parkinsonism and death of dopaminergic neurons.
Cell Death Dis. 6 , e1832, (2015) Sigma-1 receptor (σ1R) has been reported to be decreased in nigrostriatal motor system of Parkinson's disease patients. Using heterozygous and homozygous σ1R knockout (σ1R+/- and σ1R-/-) mice, we investigated the influence of σ1R deficiency on 1-methyl-4-phen... |
|
|
SCYL2 Protects CA3 Pyramidal Neurons from Excitotoxicity during Functional Maturation of the Mouse Hippocampus.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 10510-22, (2015) Neuronal death caused by excessive excitatory signaling, excitotoxicity, plays a central role in neurodegenerative disorders. The mechanisms regulating this process, however, are still incompletely understood. Here we show that the coated vesicle-associated k... |
|
|
Nitrous oxide directly inhibits action potential-dependent neurotransmission from single presynaptic boutons adhering to rat hippocampal CA3 neurons.
Brain Res. Bull. 118 , 34-45, (2015) We evaluated the effects of N2O on synaptic transmission using a preparation of mechanically dissociated rat hippocampal CA3 neurons that allowed assays of single bouton responses evoked from native functional nerve endings. We studied the effects of N2O on G... |
|
|
Frontal cortex and hippocampus neurotransmitter receptor complex level parallels spatial memory performance in the radial arm maze.
Behav. Brain Res. 289 , 157-68, (2015) Several neurotransmitter receptors have been proposed to be involved in memory formation. However, information on receptor complexes (RCs) in the radial arm maze (RAM) is missing. It was therefore the aim of this study to determine major neurotransmitter RCs ... |
|
|
Dietary magnesium restriction reduces amygdala-hypothalamic GluN1 receptor complex levels in mice.
Brain Struct. Funct. 220 , 2209-21, (2015) Reduced daily intake of magnesium (Mg(2+)) is suggested to contribute to depression. Indeed, preclinical studies show dietary magnesium restriction (MgR) elicits enhanced depression-like behaviour establishing a causal relationship. Amongst other mechanisms, ... |
|
|
The CB₁ cannabinoid receptor signals striatal neuroprotection via a PI3K/Akt/mTORC1/BDNF pathway.
Cell Death Differ. 22 , 1618-29, (2015) The CB1 cannabinoid receptor, the main molecular target of endocannabinoids and cannabis active components, is the most abundant G protein-coupled receptor in the mammalian brain. In particular, the CB1 receptor is highly expressed in the basal ganglia, mostl... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |