H-D-Asp-OH
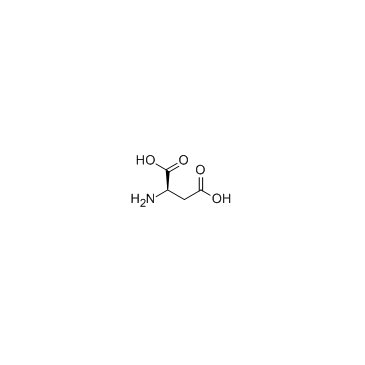
H-D-Asp-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-D-Asp-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1783-96-6 | Molecular Weight | 133.103 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 264.1±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 | Melting Point | 300ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 113.5±24.6 °C | |
|
Coupling substrate and ion binding to extracellular gate of a sodium-dependent aspartate transporter.
Nature 445 , 387-93, (2007) Secondary transporters are integral membrane proteins that catalyse the movement of substrate molecules across the lipid bilayer by coupling substrate transport to one or more ion gradients, thereby providing a mechanism for the concentrative uptake of substr... |
|
|
Oral administration of D-aspartate, but not L-aspartate, depresses rectal temperature and alters plasma metabolites in chicks.
Life Sci. 109(1) , 65-71, (2014) L-Aspartate (L-Asp) and D-aspartate (D-Asp) are physiologically important amino acids in mammals and birds. However, the functions of these amino acids have not yet been fully understood. In this study, we therefore examined the effects of L-Asp and D-Asp in ... |
|
|
Okibacterium endophyticum sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from roots of Salsola affinis C. A. Mey.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107(3) , 835-43, (2015) A white bacterial strain, designated EGI 650022(T), was isolated from the roots of Salsola affinis C. A. Mey, collected from Urumqi City, Xinjiang, north-western China. The strain was found to be aerobic, Gram-stain positive, oxidase-positive and catalase-pos... |
|
|
The prostaglandin EP1 receptor potentiates kainate receptor activation via a protein kinase C pathway and exacerbates status epilepticus.
Neurobiol. Dis. 70 , 74-89, (2014) Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) regulates membrane excitability, synaptic transmission, plasticity, and neuronal survival. The consequences of PGE2 release following seizures has been the subject of much study. Here we demonstrate that the prostaglandin E2 receptor 1... |
|
|
D-Aspartate acts as a signaling molecule in nervous and neuroendocrine systems.
Amino Acids 43(5) , 1873-86, (2012) D-Aspartate (D-Asp) is an endogenous amino acid in the central nervous and reproductive systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. High concentrations of D-Asp are found in distinct anatomical locations, suggesting that it has specific physiological roles in a... |
|
|
Biochemistry of D-aspartate in mammalian cells.
Amino Acids 32(1) , 3-11, (2007) Recent investigations have shown that D-aspartate (D-Asp) plays an important physiological role(s) in the mammalian body. Here, several recent studies of free D-Asp metabolism in mammals, focusing on cellular localization in tissues, intracellular localizatio... |
|
|
Central administration of L- and D-aspartate attenuates stress behaviors by social isolation and CRF in neonatal chicks.
Amino Acids 43(5) , 1969-76, (2012) Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of L-aspartate (L-Asp) attenuates stress responses in neonatal chicks, but the mechanism has not been clarified. In the present study, three behavioral experiments were carried out under socially isolated stress... |
|
|
Computational investigation of the substrate recognition mechanism of protein D-aspartyl (L-isoaspartyl) O-methyltransferase by docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies and application to interpret size exclusion chromatography data.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 879(29) , 3310-6, (2011) Unusual amino acid residues such as L-β-aspartyl (Asp), D-α-Asp, and D-β-Asp have been detected in proteins and peptides such as α-crystallin in the lens and β-amyloid in the brain. These residues increase with age, and hence they are associated with age-rela... |
|
|
D-Amino acids in the brain and mutant rodents lacking D-amino-acid oxidase activity.
Amino Acids 43(5) , 1811-21, (2012) D-Amino acids are stereoisomers of L-amino acids. They are often called unnatural amino acids, but several D-amino acids have been found in mammalian brains. Among them, D-serine is abundant in the forebrain and functions as a co-agonist of NMDA receptors to ... |
|
|
Immunohistochemical localization of endogenous D-Aspartate in the marine brown Alga Sargassum fusiforme.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 75(8) , 1481-4, (2011) Immunohistochemical localization (cellular localization) of endogenous D-aspartate in the marine brown alga Sargassum fusiforme was investigated by the use of a specific polyclonal antibody raised against D-aspartate. D-Aspartate immunoreactivity was evident ... |