6217-54-5
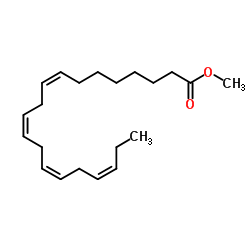
| Name | all-cis-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cervonic acid
4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z-DHA docosahexenoic acid Cervicarcin,hemihydrate cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid (4E,7E,10Z,13E,16E,19E)-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid MFCD00065722 Docosahexaenoic Acid DHA EINECS 612-950-9 |
| Description | Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid abundantly present brain and retina. It can be obtained directly from fish oil and maternal milk. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is essential for the growth and functional development of the brain in infants. DHA is also required for maintenance of normal brain function in adults. The inclusion of plentiful DHA in the diet improves learning ability and memory[1]. DHA is an essential requirement in every step of brain development like neural cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, synaptogenesis. The multiple double bonds and unique structure allow DHA to impart special membrane characteristics for effective cell signaling. Many development disorders like dyslexia, autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, schizophrenia etc. are causally related to decreased level of DHA[2]. DHA is a potent RXR ligand inducing robust RXR activation already at low micro molar concentrations. The EC50 for RXRα activation by DHA is about 5-10 μM fatty acid[3]. |
| In Vivo | Docosahexaenoic acid administration over 10 weeks significantly reduces the number of reference memory errors, without affecting the number of working memory errors, and significantly increases the docosahexaenoic acid content and the docosahexaenoic acid/arachidonic acid ratio in both the hippocampus and the cerebral cortex[4]. DHA treatment exerts neuroprotective actions on an experimental mouse model of PD. There is a decrease tendency in brain lipid oxidation of MPTP mice but it does not significantly[5]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Wistar rats are fed a fish oil-deficient diet through three generations. The young (five-week-old) male rats of the third generation are randomLy divided into two groups. Over 10 weeks, one group is perorally administered docosahexaenoic acid dissolved in 5% gum Arabic solution at 300 mg/kg/day; the other group receives a similar volume of vehicle alone. Five weeks after starting the administration, the rats are tested for learning ability related to two types of memory, reference memory and working memory, with the partially (four of eight) baited eight-arm radial maze[4]. Mice: An experimental model of Parkinson's disease is created by four intraperitoneal injections of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) (4×20 mg/kg, at 12 h intervals). Docosahexaenoic acid is given daily by gavage for 4 weeks (36 mg/kg/day). The motor activity of the mice is evaluated via the pole test. The activity of antioxidant enzymes in the brain are determined by spectrophotometric assays and the concentration of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) are measured as an index of oxidative damage[5]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 446.7±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -44ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H32O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 328.488 |
| Flash Point | 343.4±18.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 328.240234 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.78 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.521 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Light and Air Sensitive |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;half-mask respirator (US);multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S23-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NA 1993 / PGIII |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2106909090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916190090 unsaturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。general tariff:30.0% |






![2,3-bis[[(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoyl]oxy]propyl (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/357/124596-98-1.png)