teriflunomide
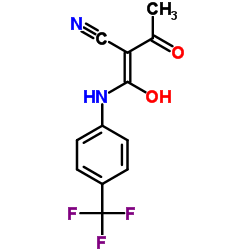
teriflunomide structure
|
Common Name | teriflunomide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 108605-62-5 | Molecular Weight | 270.207 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 363.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H9F3N2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 173.3±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Hepatic cytochrome P450s attenuate the cytotoxicity induced by leflunomide and its active metabolite A77 1726 in primary cultured rat hepatocytes.
Toxicol. Sci. 122(2) , 579-86, (2011) The Black Box Warning section of the U.S. drug label for leflunomide was recently updated to include stronger warnings about potential hepatotoxicity from this novel anti-arthritis drug. Because metabolic activation is a key mechanism for drug-induced hepatot... |
|
|
Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits lung epithelial Na+ channels by up-regulating inducible nitric-oxide synthase.
J. Biol. Chem. 284(11) , 7294-306, (2009) Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection has been shown to reduce Na+-driven alveolar fluid clearance in BALB/c mice in vivo. To investigate the cellular mechanisms by which RSV inhibits amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC), the main pathways... |
|
|
Induction of EMT-like phenotypes by an active metabolite of leflunomide and its contribution to pulmonary fibrosis.
Cell Death Differ. 17(12) , 1882-95, (2010) Drug-induced interstitial lung disease (ILD), particularly pulmonary fibrosis, is a serious clinical concern and myofibroblasts have been suggested to have a major role, with it recently being revealed that some of these myofibroblasts are derived from lung e... |
|
|
Postinfection A77-1726 treatment improves cardiopulmonary function in H1N1 influenza-infected mice.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 47(4) , 543-51, (2012) Acute respiratory disease is associated with significant morbidity and mortality in influenza. Because antiviral drugs are only effective early in infection, new agents are needed to treat nonvaccinated patients presenting with late-stage disease, particularl... |
|
|
Inhibiting effects of Leflunomide metabolite on overexpression of CD147, MMP-2 and MMP-9 in PMA differentiated THP-1 cells.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 670(1) , 304-10, (2011) Recent studies have reported elevated expression of cluster of differentiation (CD) 147 on CD14(+) monocytes of the peripheral blood of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and a correlation of CD147 expression with Disease Activity Score. Thus, CD147 ma... |
|
|
A study of the effects of substituents on the selectivity of the binding of N-arylaminomethylene malonate inhibitors to DHODH.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20(3) , 1284-7, (2010) A series of mono- and di-substituted N-arylaminomethylene malonates have been used to probe the potential of utilizing additional H-bonding contacts in the ubiquinone binding channel, for selective inhibition between either human or Plasmodium DHODH. Altered ... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of A77 1726 and leflunomide in domestic cats.
J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 35(2) , 139-46, (2012) The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of A77 1726 and leflunomide after intravenous (i.v.) and oral (p.o.) administration were evaluated in adult cats. Three treatments were administered: a single i.v. dose of A77 1726 (4 mg/kg), a single oral dose of lef... |
|
|
Suppression of immunoglobulin production by a novel dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor, S-2678.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 601(1-3) , 163-70, (2008) We discovered a novel dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHO-DH) inhibitor, S-2678 ([2-fluoro-2',5'-dimethyl-4'-[6-(3-methyl-2-butenyloxy) pyridin-3-yl] biphenyl-4-yl]-(3-methyl-2-butenyl) amine). Its inhibitory activity against DHO-DH was more potent than that of... |
|
|
Non-specific anti-proliferative effect of FTY720, a derivative of fungal metabolite from Iscaria sinclarii.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 31(2) , 160-6, (2008) FTY720 is a derivative of ISP-1 (myriocin), a fungal metabolite of the Chinese herb Iscaria sinclarii, with agonistic effect for sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor. In this study, we examined the potential adverse effect of FTY720 in terms of cell cytotoxicity ... |
|
|
Sensitization of human hepatic stellate cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by leflunomide.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 32(6) , 963-7, (2009) During the resolution phase of hepatic fibrosis, a crucial mechanism is the apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). It is necessary to find more anti-fibrosis drugs that would modulate HSCs to be more susceptible to apoptotic stimuli. Here we sh... |