prednisolone
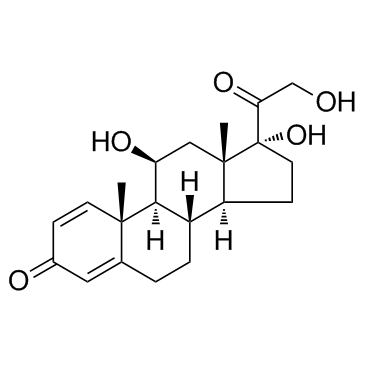
prednisolone structure
|
Common Name | prednisolone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50-24-8 | Molecular Weight | 360.444 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 570.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H28O5 | Melting Point | 240 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 313.0±26.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Fabrication of extended-release patient-tailored prednisolone tablets via fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 68 , 11-7, (2015) Rapid and reliable tailoring of the dose of controlled release tablets to suit an individual patient is a major challenge for personalized medicine. The aim of this work was to investigate the feasibility of using a fused deposition modelling (FDM) based 3D p... |
|
|
Oral lactoferrin protects against experimental candidiasis in mice.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 118(1) , 212-21, (2014) To determine the role of human lactoferrin (hLF) in protecting the oral cavities of mice against Candida albicans infection in lactoferrin knockout (LFKO(-/-)) mice was compared to wild-type (WT) mice. We also aim to determine the protective role of hLF in LF... |
|
|
Validation of cyclooxygenase-2 as a direct anti-inflammatory target of 4-O-methylhonokiol in zymosan-induced animal models.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 38 , 813-25, (2015) 4-O-methylhonokiol (MH) is known to inhibit inflammation by partially understood mechanisms. Here, the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of MH were examined using enzymatic, cellular, and animal assays. In enzymatic assays, MH inhibited COX-2 activity with an IC50... |
|
|
Development and validation of a new stability indicating reversed phase liquid chromatographic method for the determination of prednisolone acetate and impurities in an ophthalmic suspension.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 261-6, (2015) A new stability indicating reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method was developed and validated under current International Conference of Harmonisation (ICH) guidance for the determination of prednisolone acetate (PAC) and impuri... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
Detection and characterization of prednisolone metabolites in human urine by LC-MS/MS.
J. Mass Spectrom. 50(3) , 633-42, (2015) Glucocorticosteroids are prohibited in sports when used by systemic administrations (e.g. oral), whereas they are allowed using other administration ways. Strategies to discriminate between administrations routes have to be developed by doping control laborat... |
|
|
High throughput quantification of prohibited substances in plasma using thin film solid phase microextraction.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1374 , 40-9, (2014) Simple, fast and efficient sample preparation approaches that allow high-throughput isolation of various compounds from complex matrices are highly desired in bioanalysis. Particularly sought are methods that can, without sacrificing time, easily remove matri... |
|
|
Quantitative mass spectrometry imaging of emtricitabine in cervical tissue model using infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407(8) , 2073-84, (2015) A quantitative mass spectrometry imaging (QMSI) technique using infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (IR-MALDESI) is demonstrated for the antiretroviral (ARV) drug emtricitabine in incubated human cervical tissue. Method developme... |