Ethyl cinnamate
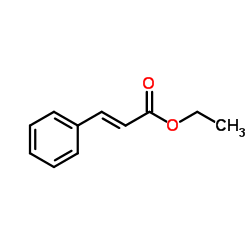
Ethyl cinnamate structure
|
Common Name | Ethyl cinnamate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 103-36-6 | Molecular Weight | 176.212 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 269.4±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H12O2 | Melting Point | 6-8 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 148.6±9.9 °C | |
|
Volatile Compounds from Grape Skin, Juice and Wine from Five Interspecific Hybrid Grape Cultivars Grown in Québec (Canada) for Wine Production.
Molecules 20 , 10980-1016, (2015) Developed from crosses between Vitis vinifera and North American Vitis species, interspecific hybrid grape varieties are becoming economically significant in northern areas, where they are now extensively grown for wine production. However, the varietal diffe... |
|
|
Novel natural product-based cinnamates and their thio and thiono analogs as potent inhibitors of cell adhesion molecules on human endothelial cells.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 , 5498-511, (2011) In the present study, we report the design and synthesis of novel analogs of cinnamates, thiocinnamates and thionocinnamates and evaluated the potencies of these analogs to inhibit TNF-α induced ICAM-1 expression on human endothelial cells. By using whole cel... |
|
|
[Effects of allelochemicals ethyl cinnamate on the growth and physiological characteristics of Chlorella pyrenoidosa].
Huan Jing Ke Xue 34(1) , 156-62, (2013) The effects of ethyl cinnamate on the growth and physiological characteristics of Chlorella pyrenoidosa were studied. The allelopathic mechanisms were explored, from views of chlorophyll a content, antioxidant enzyme activities, reactive oxygen species (ROS) ... |
|
|
Sedative activity of hexane extract of Keampferia galanga L. and its active compounds.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 120(1) , 123-5, (2008) It is well known that fragrance impacts behaviors and autonomic functions, and is increasingly used as relaxant, carminative, as well as sedative in aromatherapy. Kaempferia galanga L. is one of the popular traditional aromatic medicinal plants used in tropic... |
|
|
Pine weevil (Hylobius abietis) antifeedants from lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta).
J. Chem. Ecol. 27(11) , 2253-62, (2001) Pine weevils (Hylobius abietis) fed less on bark of lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) than on bark of Scots pine (P. sylvestris). Two pine weevil antifeedants, ethyl trans-cinnamate and ethyl 2,3-dibromo-3-phenyl-propanoate, were isolated from bark of lodgepole... |
|
|
Larvicidal activity of Kaempferia galanga rhizome phenylpropanoids towards three mosquito species.
Pest Manag. Sci. 64(8) , 857-62, (2008) This study was aimed at assessing the toxicity of ethyl cinnamate and ethyl p-methoxycinnamate (EMC) identified in Kaempferia galangal L. (Zingiberaceae) rhizome and another 12 known compounds to third-instar larvae from laboratory-reared Culex pipiens pallen... |
|
|
Sun protection enhancement of titanium dioxide crystals by the use of carnauba wax nanoparticles: the synergistic interaction between organic and inorganic sunscreens at nanoscale.
Int. J. Pharm. 322(1-2) , 161-70, (2006) Carnauba wax is partially composed of cinnamates. The rational combination of cinnamates and titanium dioxide has shown a synergistic effect to improve the sun protection factor (SPF) of cosmetic preparations. However, the mechanism of this interaction has no... |
|
|
Radical scavenging activity of lipophilized products from lipase-catalyzed transesterification of triolein with cinnamic and ferulic acids.
Lipids 44(2) , 145-52, (2009) Lipase-catalyzed transesterification of triolein with cinnamic and ferulic acids using an immobilized lipase from Candida antarctica (E.C. 3.1.1.3) was conducted to evaluate the antioxidant activity of the lipophilized products as model systems for enhanced p... |
|
|
Vasorelaxant effects of ethyl cinnamate isolated from Kaempferia galanga on smooth muscles of the rat aorta.
Planta Med. 68(7) , 655-7, (2002) From the rhizomes of Kaempferia galanga, ethyl cinnamate (EC) was isolated and its vasorelaxant effect was examined on the rat aorta. EC inhibited the tonic contractions induced by high K+ and phenylephrine (PE) in a concentration-dependent manner, with respe... |
|
|
Phytochemical investigation of labdane diterpenes from the rhizomes of Hedychium spicatum and their cytotoxic activity.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 6078-81, (2009) A comprehensive reinvestigation of chemical constituents from the rhizomes of Hedychium spicatum led to the isolation of two new labdane-type diterpene (1, 2), together with six known compounds (3-8). Their structures were established on the basis of extensiv... |