Vasorelaxant effects of ethyl cinnamate isolated from Kaempferia galanga on smooth muscles of the rat aorta.
Rozana Othman, Halijah Ibrahim, Mustafa Ali Mohd, Khalijah Awang, Anwar-Ul Hassan Gilani, Mohd Rais Mustafa
Index: Planta Med. 68(7) , 655-7, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
From the rhizomes of Kaempferia galanga, ethyl cinnamate (EC) was isolated and its vasorelaxant effect was examined on the rat aorta. EC inhibited the tonic contractions induced by high K+ and phenylephrine (PE) in a concentration-dependent manner, with respective IC50 values of 0.30 +/- 0.05 mM and 0.38 +/- 0.04 mM. The relaxant effect against PE-induced contractions was greater in the presence of endothelium. Pre-treatment of the aorta with methylene blue and indomethacin significantly reduced the relaxant effect. These results suggest that the inhibitory effects of EC may involve inhibition of Ca2+ influx into vascular cells and release of nitric oxide (NO) and prostacyclin from the endothelial cells. Thus, the vasorelaxant effect of EC mediated through multiple pathways may explain the traditional use of the parent plant in treating hypertension.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
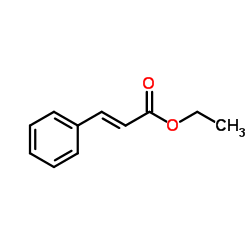 |
Ethyl cinnamate
CAS:103-36-6 |
C11H12O2 |
|
Volatile Compounds from Grape Skin, Juice and Wine from Five...
2015-01-01 [Molecules 20 , 10980-1016, (2015)] |
|
Novel natural product-based cinnamates and their thio and th...
2011-11-01 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 , 5498-511, (2011)] |
|
[Effects of allelochemicals ethyl cinnamate on the growth an...
2013-01-01 [Huan Jing Ke Xue 34(1) , 156-62, (2013)] |
|
Sedative activity of hexane extract of Keampferia galanga L....
2008-10-30 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 120(1) , 123-5, (2008)] |
|
Pine weevil (Hylobius abietis) antifeedants from lodgepole p...
2001-11-01 [J. Chem. Ecol. 27(11) , 2253-62, (2001)] |