Journal of Chemical Ecology
2001-11-01
Pine weevil (Hylobius abietis) antifeedants from lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta).
K Bratt, K Sunnerheim, H Nordenhem, G Nordlander, B Langström
Index: J. Chem. Ecol. 27(11) , 2253-62, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Pine weevils (Hylobius abietis) fed less on bark of lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) than on bark of Scots pine (P. sylvestris). Two pine weevil antifeedants, ethyl trans-cinnamate and ethyl 2,3-dibromo-3-phenyl-propanoate, were isolated from bark of lodgepole pine. These two compounds significantly reduced pine weevil feeding in a laboratory bioassay. In field assays, the second compound significantly decreased pine weevil damage on planted seedlings. Ethyl 2,3-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoate has not previously been reported as a natural product.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
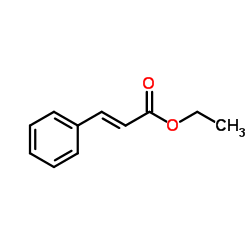 |
Ethyl cinnamate
CAS:103-36-6 |
C11H12O2 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Volatile Compounds from Grape Skin, Juice and Wine from Five...
2015-01-01 [Molecules 20 , 10980-1016, (2015)] |
|
Novel natural product-based cinnamates and their thio and th...
2011-11-01 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 , 5498-511, (2011)] |
|
[Effects of allelochemicals ethyl cinnamate on the growth an...
2013-01-01 [Huan Jing Ke Xue 34(1) , 156-62, (2013)] |
|
Sedative activity of hexane extract of Keampferia galanga L....
2008-10-30 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 120(1) , 123-5, (2008)] |
|
Larvicidal activity of Kaempferia galanga rhizome phenylprop...
2008-08-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 64(8) , 857-62, (2008)] |