Suprofen
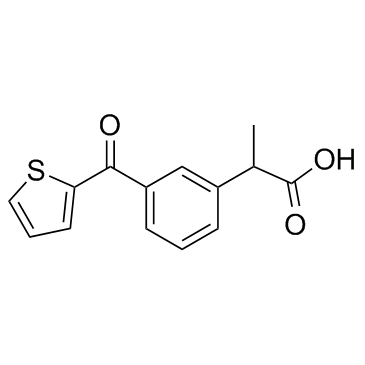
Suprofen structure
|
Common Name | Suprofen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 40828-46-4 | Molecular Weight | 260.308 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 442.6±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H12O3S | Melting Point | 278ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 221.5±24.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Suprofen, a new peripheral analgesic.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 214(1) , 16-23, (1980) The antinociceptive properties of suprofen [alpha-methyl-4-(thienylcarbonyl)benzene acetic acid] are described in a pathologically induced hyperalgesic model, the rat adjuvant arthritis flexion test. By using this assay, suprofen was characterized as an orall... |
|
|
Suprofen: the pharmacology and clinical efficacy of a new non-narcotic peripheral analgesic.
Clin. Rheum. Dis. 10(2) , 353-68, (1984) Suprofen is a potent, peripherally-acting, non-narcotic analgesic agent. The mechanism of action of the compound involves inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis and, perhaps, direct antagonism of the peripheral, pain inducing actions of prostaglandins, brad... |
|
|
Suprofen, a potent antagonist of acetic acid-induced writhing in rats.
Arzneimittelforschung 25(10) , 1505-9, (1975) A new standardized acetic acid-induced writhing test in rats is described in detail and its methodology is discussed briefly. The described method has proved to be useful for evaluating the anti-writhing activity of narcotic analgesics, non-narcotic anti-infl... |
|
|
Renal effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Agents Actions. Suppl. 24 , 95-106, (1988) All nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit cyclooxygenase, and consequently renal functions dependent upon prostaglandin synthesis can be affected. Fortunately, renal function in normal individuals is relatively independent of the PG system, an... |
|
|
Significantly Different Covalent Binding of Oxidative Metabolites, Acyl Glucuronides, and S-Acyl CoA Conjugates Formed from Xenobiotic Carboxylic Acids in Human Liver Microsomes.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 28(5) , 886-96, (2015) Xenobiotic carboxylic acids may be metabolized to oxidative metabolites, acyl glucuronides, and/or S-acyl-CoA thioesters (CoA conjugates) in vitro, e.g., in hepatocytes, and in vivo. These metabolites can potentially be reactive species and bind covalently to... |
|
|
Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P450 2C9 by tienilic acid and (+/-)-suprofen: a comparison of kinetics and probe substrate selection.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 37(1) , 59-65, (2009) In vitro experiments were conducted to compare k(inact), K(I) and inactivation efficiency (k(inact)/K(I)) of cytochrome P450 (P450) 2C9 by tienilic acid and (+/-)-suprofen using (S)-flurbiprofen, diclofenac, and (S)-warfarin as reporter substrates. Although t... |