Suprofen: the pharmacology and clinical efficacy of a new non-narcotic peripheral analgesic.
E L Tolman, M E Rosenthale, R J Capetola, J L McGuire
Index: Clin. Rheum. Dis. 10(2) , 353-68, (1984)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Suprofen is a potent, peripherally-acting, non-narcotic analgesic agent. The mechanism of action of the compound involves inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis and, perhaps, direct antagonism of the peripheral, pain inducing actions of prostaglandins, bradykinin and other pain mediators. Suprofen at a dose of 200 mg appears to be equal or greater in efficacy as an analgesic modality than those of ibuprofen, propoxyphene, naproxen and diflunisal or a combination of 650 mg aspirin plus 60 mg codeine. Its clinical utility has been amply demonstrated in the treatment of a number of types of pain including general and orthopedic surgery, episiotomy, post-partum pain, dysmenorrhea, dental pain and musculoskeletal disorders. Suprofen represents a new class of orally effective nonnarcotic analgesics with potential for effective clinical use in the treatment of pain.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
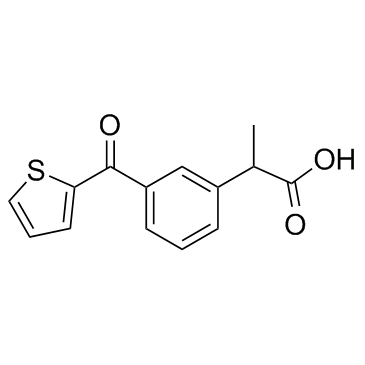 |
Suprofen
CAS:40828-46-4 |
C14H12O3S |
|
Suprofen, a new peripheral analgesic.
1980-07-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 214(1) , 16-23, (1980)] |
|
Suprofen, a potent antagonist of acetic acid-induced writhin...
1975-10-01 [Arzneimittelforschung 25(10) , 1505-9, (1975)] |
|
Renal effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
1988-01-01 [Agents Actions. Suppl. 24 , 95-106, (1988)] |
|
Significantly Different Covalent Binding of Oxidative Metabo...
2015-05-18 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 28(5) , 886-96, (2015)] |
|
Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P450 2C9 by tieni...
2009-01-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 37(1) , 59-65, (2009)] |