Levulinic acid
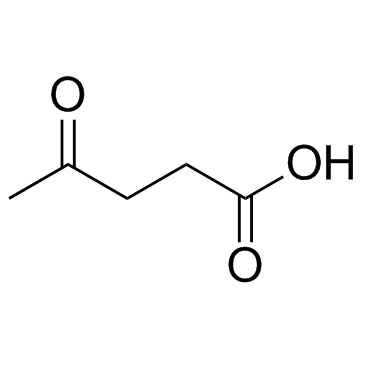
Levulinic acid structure
|
Common Name | Levulinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 123-76-2 | Molecular Weight | 116.115 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 242.9±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O3 | Melting Point | 30-33 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 137.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Detoxification of biomass hydrolysates with nucleophilic amino acids enhances alcoholic fermentation.
Bioresour. Technol. 186 , 106-13, (2015) Carbonyl compounds generated in biomass pretreatment hinder the biochemical conversion of biomass hydrolysates to biofuels. A novel approach of detoxifying hydrolysates with amino acids for ethanol production was developed. Among the 20 amino acids assessed f... |
|
|
Effectiveness of levulinic acid and sodium dodecyl sulfate employed as a sanitizer during harvest or packing of cantaloupes contaminated with Salmonella Poona.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 207 , 71-6, (2015) Freshly harvested Eastern variety cantaloupes (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus cv. Athena) were subjected to three different harvest and wash treatments to examine conditions under which the efficacy of the sanitizer, levulinic acid (LV) plus sodium dodecyl ... |
|
|
Differential expression of small RNAs under chemical stress and fed-batch fermentation in E. coli.
BMC Genomics 16 , 1051, (2015) Bacterial small RNAs (sRNAs) are recognized as posttranscriptional regulators involved in the control of bacterial lifestyle and adaptation to stressful conditions. Although chemical stress due to the toxicity of precursor and product compounds is frequently ... |
|
|
Microbial synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate using seaweed-derived crude levulinic acid as co-nutrient.
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 72 , 487-94, (2014) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from Jatropha biodiesel residues, namely crude glycerol and oil cake hydrolysate, has been reported previously. Halomonas hydrothermalis (MTCC accession no. 5445; NCBI Genbank accession no. GU938192), a wild marine s... |
|
|
Pyrochars from bioenergy residue as novel bio-adsorbents for lignocellulosic hydrolysate detoxification.
Bioresour. Technol. 187 , 379-86, (2015) The robust supramolecular structure of biomass often requires severe pretreatments conditions to produce soluble sugars. Nonetheless, these processes generate some inhibitory compounds (i.e. furans compounds and aliphatic acids) deriving mainly from sugars de... |
|
|
Process development for biological production of butanol from Eastern redcedar.
Bioresour. Technol. 176 , 88-97, (2014) Eastern redcedar is an invasive softwood species in Oklahoma and across grasslands in the Central Plains of the United States and potential feedstock for butanol production. Butanol has higher energy content than ethanol and can be upgraded to jet and diesel ... |
|
|
Acid-catalyzed hydrothermal severity on the fractionation of agricultural residues for xylose-rich hydrolyzates.
Bioresour. Technol. 132 , 84-90, (2013) The objective of this work was to investigate the feasibility of acid-catalyzed hydrothermal fractionation for maximum solubilization of the hemicellulosic portion of three agricultural residues. The fractionation conditions converted into combined severity f... |
|
|
Co-immobilization of semaphorin3A and nerve growth factor to guide and pattern axons.
Acta Biomater. 28 , 33-44, (2015) Immobilization of axon guidance cues offers a powerful tissue regenerative strategy to control the presentation and spatial location of these biomolecules. We use our previously developed immobilization strategy to specifically tether recombinant biotinylated... |
|
|
Ozone detoxification of steam-pretreated Norway spruce.
Biotechnol. Biofuels 8 , 196, (2015) Pretreatment of lignocellulose for biochemical conversion commonly results in formation of by-products that inhibit microorganisms and cellulolytic enzymes. To make bioconversion processes more efficient, inhibition problems can be alleviated through conditio... |
|
|
Nanotherapeutics shielded with a pH responsive polymeric layer.
Physiol. Res. 64 Suppl 1 , S29-40, (2015) Efficient intravenous delivery is the greatest single hurdle, with most nanotherapeutics frequently found to be unstable in the harsh conditions of the bloodstream. In the case of nanotherapeutics for gene delivery, viral vectors are often avidly recognized b... |