| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
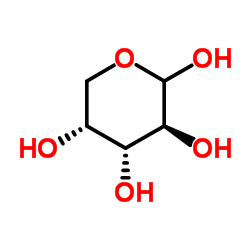 |
D-Arabinose
CAS:10323-20-3 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
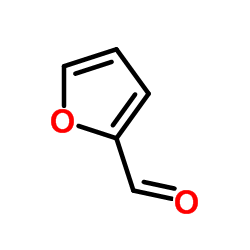 |
Furfural
CAS:98-01-1 |
|
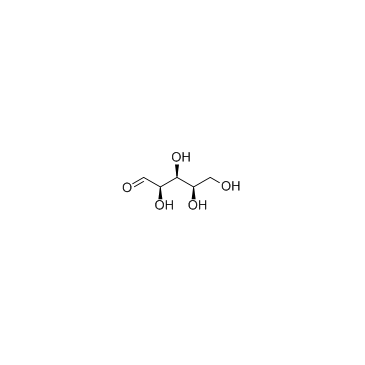 |
D-(+)-Xylose
CAS:58-86-6 |
|
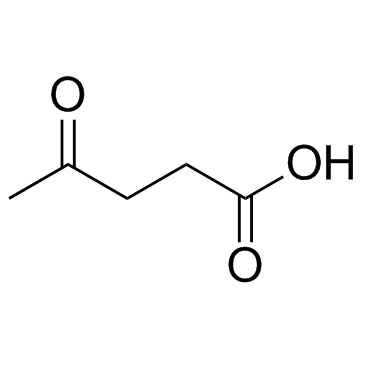 |
Levulinic acid
CAS:123-76-2 |
|
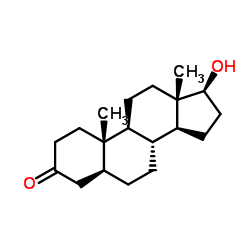 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
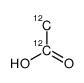 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |