D-(+)-Xylose
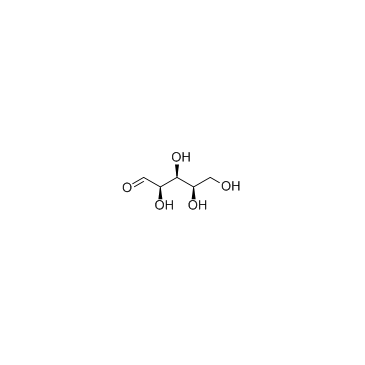
D-(+)-Xylose structure
|
Common Name | D-(+)-Xylose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58-86-6 | Molecular Weight | 150.130 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 415.5±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10O5 | Melting Point | 148-158 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 219.2±23.3 °C | |
Use of D-(+)-XyloseXylose, a natural product, can be catalyzed into xylulose by xylose isomerase, and it is the key step for anaerobic ethanolic fermentation of xylose. |
| Name | aldehydo-D-xylose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Xylose, a natural product, can be catalyzed into xylulose by xylose isomerase, and it is the key step for anaerobic ethanolic fermentation of xylose. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 415.5±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 148-158 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 150.130 |
| Flash Point | 219.2±23.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 150.052826 |
| PSA | 90.15000 |
| LogP | -2.39 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.544 |
| InChIKey | PYMYPHUHKUWMLA-VPENINKCSA-N |
| SMILES | O=CC(O)C(O)C(O)CO |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25-36-26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | ZF2285000 |
| HS Code | 2940000000 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2940000000 |
|---|
|
High-yield hydrogen production from biomass by in vitro metabolic engineering: Mixed sugars coutilization and kinetic modeling.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112(16) , 4964-9, (2015) The use of hydrogen (H2) as a fuel offers enhanced energy conversion efficiency and tremendous potential to decrease greenhouse gas emissions, but producing it in a distributed, carbon-neutral, low-co... |
|
|
Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. polysaccharide ameliorates hyperglycemia, hyperlipemia and vascular inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 164 , 229-38, (2015) Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (RG) has been widely used as traditional Chinese herbal medicine for treatment of diabetes and its complications. The polysaccharide fraction of RG has been proposed ... |
|
|
L-citrulline production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum from glucose and alternative carbon sources.
AMB Express 4 , 85, (2015) L-citrulline plays an important role in human health and nutrition and is an intermediate of the L-arginine biosynthetic pathway. L-citrulline is a by-product of L-arginine production by Corynebacteri... |
| (D)-Xylose |
| D(+)-Xylose |
| D-Xyluose |
| aldehydo-D-xylose |
| d-xylos |
| XYLOSE,CP |
| (2R,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxypentanal |
| D-(+)-Xylose |
| Xylomed |
| WOOD SUGAR |
| XYLOSE-D |
| Xylose |
| D-Xylose |
| Xylo-Pfan |
| Xylopyranose |
| D-XYL |
| Xylose, D- |
| EINECS 200-400-7 |
| (+)-Xylose |
| MFCD00151475 |
 CAS#:87-99-0
CAS#:87-99-0![25(S)-ruscogenin 1-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→2)-[β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-D-fucopyranoside Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/141/1486510-48-8.png) CAS#:1486510-48-8
CAS#:1486510-48-8 CAS#:9004-34-6
CAS#:9004-34-6 CAS#:1244548-36-4
CAS#:1244548-36-4 CAS#:2001-96-9
CAS#:2001-96-9 CAS#:19694-88-3
CAS#:19694-88-3 CAS#:10343-54-1
CAS#:10343-54-1 CAS#:10173-38-3
CAS#:10173-38-3 CAS#:551-84-8
CAS#:551-84-8 CAS#:1114-34-7
CAS#:1114-34-7 CAS#:10323-20-3
CAS#:10323-20-3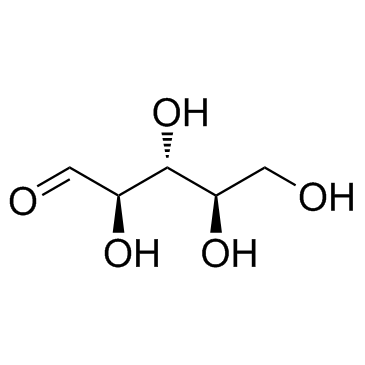 CAS#:50-69-1
CAS#:50-69-1 CAS#:3068-31-3
CAS#:3068-31-3 CAS#:74015-70-6
CAS#:74015-70-6 CAS#:137-00-8
CAS#:137-00-8 CAS#:3188-00-9
CAS#:3188-00-9
