Zalcitabine
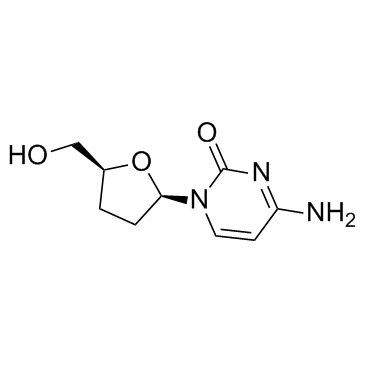
Zalcitabine structure
|
Common Name | Zalcitabine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7481-89-2 | Molecular Weight | 211.218 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 415.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13N3O3 | Melting Point | 217-218 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 204.8±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Absence of a universal mechanism of mitochondrial toxicity by nucleoside analogs.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 2531-9, (2007) Nucleoside analogs are associated with various mitochondrial toxicities, and it is becoming increasingly difficult to accommodate these differences solely in the context of DNA polymerase gamma inhibition. Therefore, we examined the toxicities of zidovudine (... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Prediction of drug intestinal absorption by new linear and non-linear QSPR.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 , 218-28, (2011) In order to minimize the high attrition rate that usually characterizes drug research and development projects, current medicinal chemists aim to characterize both pharmacological and ADME profiles at the beginning of drug R&D initiatives. Thus, the developme... |
|
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared and assayed 33 coumarin derivatives, and the theoretical pr... |
|
|
Synthesis of fluorescent nucleoside analogs as probes for 2'-deoxyribonucleoside kinases.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 , 841-3, (2010) We are reporting on the synthesis of fluorescent nucleoside analogs with modified sugar moieties (e.g., sugars other than ribose and 2'-deoxyribose). Four novel derivatives of the fluorescent thymidine analog 6-methyl-3-(beta-D-2'-deoxyribofuranosyl) furano-[... |
|
|
FDA-approved drug labeling for the study of drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Discov. Today 16 , 697-703, (2011) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a leading cause of drugs failing during clinical trials and being withdrawn from the market. Comparative analysis of drugs based on their DILI potential is an effective approach to discover key DILI mechanisms and risk fact... |