| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
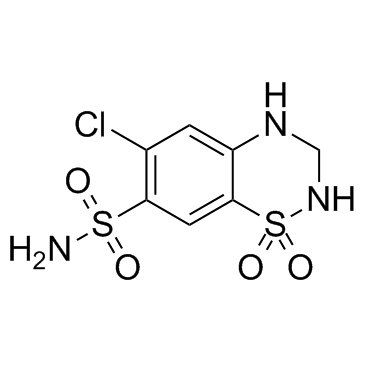 |
Hydrochlorothiazide
CAS:58-93-5 |
|
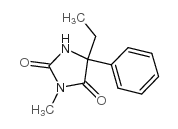 |
Mephenytoin
CAS:50-12-4 |
|
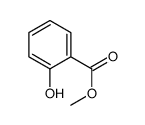 |
Methyl salicylate
CAS:90045-28-6 |
|
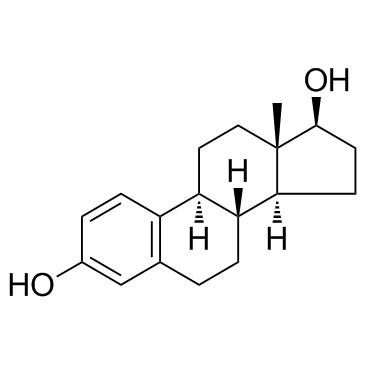 |
beta-Estradiol
CAS:50-28-2 |
|
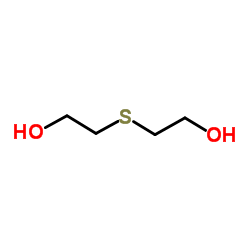 |
thiodiglycol
CAS:111-48-8 |
|
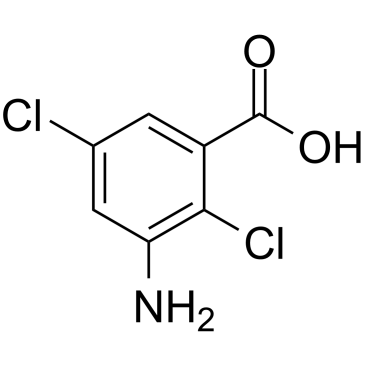 |
chloramben
CAS:133-90-4 |
|
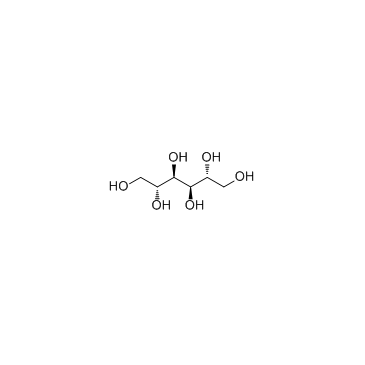 |
D-Mannitol
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
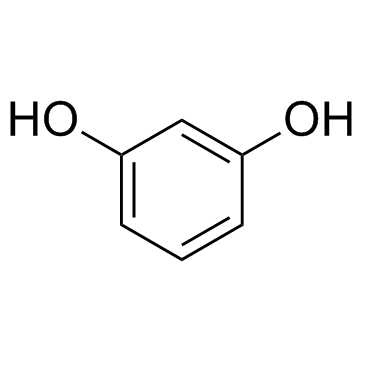 |
Resorcine
CAS:108-46-3 |
|
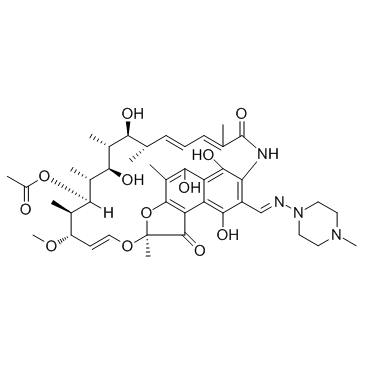 |
Rifampicin
CAS:13292-46-1 |
|
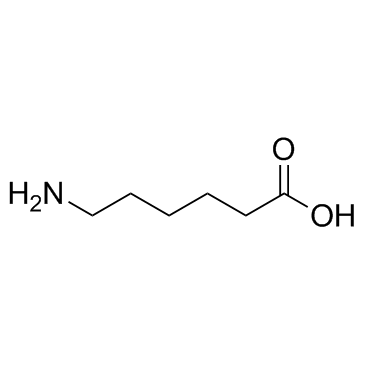 |
6-Aminocaproic acid
CAS:60-32-2 |