Mephenytoin
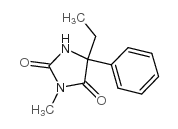
Mephenytoin structure
|
Common Name | Mephenytoin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50-12-4 | Molecular Weight | 218.25200 | |
| Density | 1.154g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H14N2O2 | Melting Point | 135-138ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Multi-target spectral moment QSAR versus ANN for antiparasitic drugs against different parasite species.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 2225-31, (2010) There are many of pathogen parasite species with different susceptibility profile to antiparasitic drugs. Unfortunately, almost QSAR models predict the biological activity of drugs against only one parasite species. Consequently, predicting the probability wi... |
|
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared and assayed 33 coumarin derivatives, and the theoretical pr... |
|
|
Assessment of urinary mephenytoin metrics to phenotype for CYP2C19 and CYP2B6 activity.
Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64(4) , 387-98, (2008) (S)-Mephenytoin is selectively metabolised to (S)-4'-hydroxymephenytoin by CYP2C19. The urinary excretion of 4'-hydroxymephenytoin reflects the activity of individual enzymes. We evaluated fractioned urinary collection and beta-glucuronidase pre-treatment in ... |
|
|
Generation of mice transgenic for human CYP2C18 and CYP2C19: characterization of the sexually dimorphic gene and enzyme expression.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 36(5) , 955-62, (2008) CYP2C19 is an important enzyme for human drug metabolism, and it also participates in the metabolism of endogenous substrates, whereas the CYP2C18 enzyme is not expressed in human liver despite high mRNA expression. Mice transgenic for the human CYP2C18 and C... |
|
|
Artemisinin antimalarials moderately affect cytochrome P450 enzyme activity in healthy subjects.
Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 21(3) , 307-16, (2007) The aim of this study was to investigate which principal human cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes are affected by artemisinin and to what degree the artemisinin derivatives differ with respect to their respective induction and inhibition capacity. Seventy-five ... |
|
|
Development of an in vitro drug-drug interaction assay to simultaneously monitor five cytochrome P450 isoforms and performance assessment using drug library compounds.
J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 58(3) , 206-14, (2008) Inhibition of cytochrome P450 (CYP) is a principal mechanism for metabolism-based drug-drug interactions (DDIs). This article describes a robust, high-throughput CYP-mediated DDI assay using a cocktail of 5 clinically relevant probe substrates with quantifica... |
|
|
How did phenobarbital's chemical structure affect the development of subsequent antiepileptic drugs (AEDs)?
Epilepsia 53 Suppl 8 , 3-11, (2012) Phenobarbital has been in clinical use as an antiepileptic drug (AED) since 1912. The initial clinical success of phenobarbital and other barbiturates affected the design of subsequent AEDs (e.g., phenytoin, primidone, ethosuximide), developed between 1938 an... |
|
|
Predicted metabolic drug clearance with increasing adult age.
Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 75(4) , 1019-28, (2013) To determine the effect of increasing adult age on predicted metabolic drug clearance.Predicted metabolic drug clearances (CLPT ) were determined using in vitro-in vivo extrapolation coupled with physiological-based pharmacokinetic modelling and simulation (I... |