4-azidophenacyl bromide
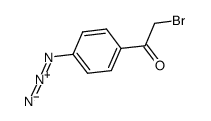
4-azidophenacyl bromide structure
|
Common Name | 4-azidophenacyl bromide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 57018-46-9 | Molecular Weight | 240.05700 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6BrN3O | Melting Point | 64-65ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Direct identification of on-bead peptides using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic barcoding system for high-throughput bioanalysis.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 10144, (2015) Recently, preparation and screening of compound libraries remain one of the most challenging tasks in drug discovery, biomarker detection, and biomolecular profiling processes. So far, several distinct encoding/decoding methods such as chemical encoding, grap... |
|
|
The σ70 region 1.2 regulates promoter escape by unwinding DNA downstream of the transcription start site.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41(8) , 4565-72, (2013) The mechanisms of abortive synthesis and promoter escape during initiation of transcription are poorly understood. Here, we show that, after initiation of RNA synthesis, non-specific interaction of σ(70) region 1.2, present in all σ(70) family factors, with t... |
|
|
4-Bromophenacyl bromide specifically inhibits rhoptry secretion during Toxoplasma invasion.
PLoS ONE 4(12) , e8143, (2009) Toxoplasma gondii is a eukaryotic parasite of the phylum Apicomplexa that is able to infect a wide variety of host cells. During its active invasion process it secretes proteins from discrete secretory organelles: the micronemes, rhoptries and dense granules.... |
|
|
Photoaffinity reagents for use with pepsin and other carboxyl proteases.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 111(2) , 630-5, (1983) Two compounds have been designed to serve as photoaffinity reagents for use with carboxyl proteases. 1,2-Epoxy-3-(4'-azido-2'-nitrophenoxy)propane has been synthesized and shown to react with porcine pepsin in the same fashion as the traditional inhibitor 1,2... |
|
|
Association of thioredoxin with the inner membrane and adhesion sites in Escherichia coli.
J. Bacteriol. 169(6) , 2659-66, (1987) The intracellular localization of thioredoxin in Escherichia coli was determined by immunoelectron microscopy and correlated to previous biochemical data which had suggested that thioredoxin resides at inner-outer membrane adhesion sites. Since a considerable... |
|
|
Crosslinking of phenylalanyl-tRNA to the ribosomal A site via a photoaffinity probe attached to the 4-thiouridine residue is exclusively to ribosomal protein S19.
J. Mol. Biol. 172(1) , 77-86, (1984) Phe-tRNA of Escherichia coli, specifically derivatized at the S4U8 position with the 9 A long p-azidophenacyl photoaffinity probe, can be crosslinked to 30 S ribosomal protein when the tRNA is placed at the ribosomal A site. This protein has now been identifi... |
|
|
Covalent crosslinking of Escherichia coli phenylalanyl-tRNA and valyl-tRNA to the ribosomal A site via photoaffinity probes attached to the 4-thiouridine residue.
J. Mol. Biol. 172(1) , 57-76, (1984) tRNAPhe and tRNAVal of Escherichia coli were derivatized at the S4U8 position with p-azidophenacyl and p-azidophenacylacetate photoaffinity probes. The modified tRNAs could still function efficiently in all of the partial reactions of protein synthesis except... |
|
|
4-Azido[3,5-3H]phenacyl bromide, a versatile bifunctional reagent for photoaffinity radiolabeling. Synthesis of prostaglandin 4-azido[3,5-3H]phenacyl esters.
Bioconjug. Chem. 1(5) , 363-4, (1990)
|
|
|
Structure determination by directed photo-cross-linking in large RNA molecules with site-specific psoralen.
Meth. Enzymol. 318 , 104-18, (2000)
|
|
|
Probing contacts between the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and nucleic acid by site-specific photocross-linking.
J. Biol. Chem. 275(21) , 16015-22, (2000) Cys(38) and Cys(280) of p66/p51 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase (HIV-1 RT) can be converted to Ser without affecting enzyme function. We have exploited this feature to construct and purify "monocysteine" RT derivatives for site-speci... |