Pralidoxime Iodide
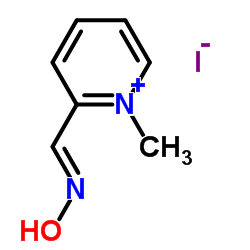
Pralidoxime Iodide structure
|
Common Name | Pralidoxime Iodide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94-63-3 | Molecular Weight | 264.064 | |
| Density | 1.7439 g/ml | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9IN2O | Melting Point | 220 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A trivalent approach for determining in vitro toxicology: Examination of oxime K027.
J. Appl. Toxicol. 35(2) , 219-27, (2014) Unforeseen toxic effects contribute to compound attrition during preclinical evaluation and clinical trials. Consequently, there is a need to correlate in vitro toxicity to in vivo and clinical outcomes quickly and effectively. We propose an expedited evaluat... |
|
|
Reactions of methylphosphonic difluoride with human acetylcholinesterase and oximes--Possible therapeutic implications.
Toxicol. Lett. 231(1) , 92-8, (2014) Highly toxic organophosphorus (OP) nerve agents are well characterized regarding chemical, biological and toxicological properties and the effectiveness of standard atropine and oxime therapy. Open literature data on the key nerve agent precursor methylphosph... |
|
|
An in vivo zebrafish screen identifies organophosphate antidotes with diverse mechanisms of action.
J. Biomol. Screen. 18(1) , 108-15, (2013) Organophosphates are a class of highly toxic chemicals that includes many pesticides and chemical weapons. Exposure to organophosphates, either through accidents or acts of terrorism, poses a significant risk to human health and safety. Existing antidotes, in... |
|
|
Chlorpyrifos is associated with slower serum cholinesterase recovery in acute organophosphate-poisoned patients.
Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 51(5) , 402-8, (2013) Organophosphate poisoning (OPP) accounts for 200,000 deaths annually in developing countries. Serum cholinesterase (SChE) is of diagnostic value in patients with OPP and is checked repeatedly during the course of treatment. This study aimed to investigate the... |
|
|
Effect of different oximes on rat and human cholinesterases inhibited by methamidophos: a comparative in vitro and in silico study.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 111(6) , 362-70, (2012) Methamidophos is one of the most toxic organophosphorus (OP) compounds. It acts via phosphorylation of a serine residue in the active site of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), leading to enzyme inactivation. Different oximes have b... |
|
|
Reactivation kinetics of 31 structurally different bispyridinium oximes with organophosphate-inhibited human butyrylcholinesterase.
Arch. Toxicol. 89(3) , 405-14, (2015) Organophosphorus compounds (OP) are bound to human butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and endogenous or exogenous BChE may act as a stoichiometric scavenger. Adequate amounts of BChE are required to minimize toxic OP effects. Simultaneous administration of BChE and... |
|
|
Phase II study of magnesium sulfate in acute organophosphate pesticide poisoning.
Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 51(1) , 35-40, (2013) Acute organophosphorus (OP) poisoning is relatively common and a major cause of death from poisoning in developing countries. Magnesium has been shown to be of benefit in animal models.We conducted a phase II study of bolus doses of (MgSO4) in 50 patients wit... |
|
|
Recurrent neonatal organophoshorus poisoning.
Indian Pediatr. 49(9) , 752-3, (2012) Organophosphorus poisoning in neonates is extremely rare and needs high index of suspicion to diagnose it. The clinical presentation is often confused with the features of sepsis like apnea, copious oral secretions, diarrhea, letharginess, seizures. There may... |
|
|
A retrospective analysis of acute organophosphorus poisoning cases admitted to the tertiary care teaching hospital in South India.
Ann. Afr. Med. 13(2) , 71-5, (2014) We have herein reported our experience with the pattern of presentation of cases of acute organophosphorus (OP) poisoning cases in a tertiary care hospital.This retrospective study evaluated the hospital records of patients with acute OP poisoning. In a pre-s... |
|
|
Body mass index as a prognostic factor in organophosphate-poisoned patients.
Am. J. Emerg. Med. 32(7) , 693-6, (2014) Organophosphate poisoning is a serious clinical entity and considerable morbidity and mortality. Several factors have been identified to predict outcomes of organophosphate poisoning. Organophosphates are lipophilic and therefore predicted to have a large vol... |