Sodium polymethacrylate
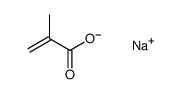
Sodium polymethacrylate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium polymethacrylate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 54193-36-1 | Molecular Weight | 108.07100 | |
| Density | 1.023g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 160.5ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H5NaO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 74.2ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A novel pH-dependant and double crosslinked polymethacrylate-based polysphere matrix for enteric delivery of isoniazid.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 18(5) , 1066-77, (2013) This study aimed at developing double crosslinked isoniazid (INH)-loaded polymethyl-methacrylate-ethylcellulose (PMMA-EC) polyspheres for rate-controlled enteric drug delivery. A PMMA solution was manipulated with the addition of EC to produce polyspheres by ... |
|
|
Poly(methacrylic acid)-grafted chitosan microspheres via surface-initiated ATRP for enhanced removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution.
J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 405 , 171-82, (2013) Cross-linked chitosan (CCS) microspheres tethered with pH-sensitive poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) brushes were developed for the efficient removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Functional PMAA brushes containing dense and active carboxyl groups (COOH... |
|
|
Strain screening, fermentation, separation, and encapsulation for production of nattokinase functional food.
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 168(7) , 1753-64, (2012) This study presents a novel and integrated preparation technology for nattokinase functional food, including strain screening, fermentation, separation, and encapsulation. To rapidly screen a nattokinase-productive strain, PCR-based screening method was combi... |
|
|
pH-dependent control of particle motion through surface interactions with patterned polymer brush surfaces.
Langmuir 28(36) , 12955-61, (2012) In this Article, we show that inclined silicon surfaces patterned with poly(methacrylic acid) brushes are able to control the position and movement of 20 μm silica particles, which are propelled across the patterned surface by sedimentation forces. Three diff... |
|
|
Design of sustained release fine particles using two-step mechanical powder processing: particle shape modification of drug crystals and dry particle coating with polymer nanoparticle agglomerate.
Int. J. Pharm. 453(2) , 523-32, (2013) We attempted to prepare sustained release fine particles using a two-step mechanical powder processing method; particle-shape modification and dry particle coating. First, particle shape of bulk drug was modified by mechanical treatment to yield drug crystals... |
|
|
KGM and PMAA based pH-sensitive interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel for controlled drug release.
Carbohydr. Polym. 97(2) , 565-70, (2013) Sequential interpenetrating polymer networks (IPN) hydrogels based on konjac glucomannan (KGM) and poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) were prepared by immersion of a solution of methacrylic acid (MAA) monomer with cross-linker N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAAm) a... |
|
|
Thrombin immobilization to methacrylic acid grafted poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and its in vitro application.
Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 43(1) , 48-59, (2013) Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) is nontoxic and biodegradable, with good biocompatibility and potential support for long-term implants. For this reason, it is a good support for enzyme immobilization. Enzyme immobilization could not be done directly because poly(3-hy... |
|
|
A sulfated glycosaminoglycan array for molecular interactions between glycosaminoglycans and growth factors or anti-glycosaminoglycan antibodies.
Anal. Biochem. 435(2) , 123-30, (2013) Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) take part in numerous biological processes by binding to protein molecules and functionally regulating protein-ligand interactions; therefore, molecular interactions of GAGs have been studied by several methods, including surface pla... |
|
|
Noneluting enzymatic antibiofilm coatings.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4(9) , 4708-16, (2012) We developed a highly efficient, biocompatible surface coating that disperses bacterial biofilms through enzymatic cleavage of the extracellular biofilm matrix. The coating was fabricated by binding the naturally existing enzyme dispersin B (DspB) to surface-... |
|
|
Principles and applications of steric exclusion chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1270 , 162-70, (2012) We introduce a chromatography method for purification of large proteins and viruses that works by capturing them at a non-reactive hydrophilic surface by their mutual steric exclusion of polyethylene glycol (PEG). No direct chemical interaction between the su... |