D-Glucosamine-6-sulfate
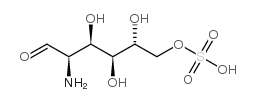
D-Glucosamine-6-sulfate structure
|
Common Name | D-Glucosamine-6-sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91674-26-9 | Molecular Weight | 259.23 | |
| Density | 1.757g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO8S | Melting Point | 60-162 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Human ficolin-2 recognition versatility extended: an update on the binding of ficolin-2 to sulfated/phosphated carbohydrates.
FEBS Lett. 588(24) , 4694-700, (2014) Ficolin-2 has been reported to bind to DNA and heparin, but the mechanism involved has not been thoroughly investigated. X-ray studies of the ficolin-2 fibrinogen-like domain in complex with several new ligands now show that sulfate and phosphate groups are p... |
|
|
Characteristics of the glmS ribozyme suggest only structural roles for divalent metal ions.
RNA 12 , 607 - 619, (2006) The glmS ribozyme is a riboswitch class that occurs in certain Gram-positive bacteria, where it resides within mRNAs encoding glucosamine 6-phosphate synthase. Members of this self-cleaving ribozyme class rapidly catalyze RNA transesterification upon binding ... |
|
|
The effects of glucosamine sulfate on intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus cells in vitro.
Spine J. 15 , 1339-46, (2015) Glucosamine has gained widespread use among patients, despite inconclusive efficacy data. Inconsistency in the clinical literature may be related to lack of understanding of the effects of glucosamine on the intervertebral disc, and therefore, improper patien... |
|
|
Binding of heparin to antithrombin III: a chemical proof of the critical role played by a 3-sulfated 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose residue.
Carbohydr. Res. 179 , 163-72, (1988) Known methyl (prop-1-enyl 2,3-di-O-benzyl-alpha-D-glucopyranosid)uronate was first converted into methyl (prop-1-enyl 2,3-di-O-benzyl-4-O-levulinyl-alpha-D-gluco-pyranosid)uro nat e. Acid hydrolysis, followed by treatment with (bromomethylene)-dimethylammoniu... |
|
|
Common binding sites for beta-amyloid fibrils and fibroblast growth factor-2 in heparan sulfate from human cerebral cortex.
J. Biol. Chem. 274(43) , 30631-5, (1999) Heparan sulfate found in the cerebral plaques of Alzheimer's disease binds to beta-amyloid (Abeta) fibrils. This interaction has been proposed to enhance fibril deposition and mediate Abeta-induced glia activation and neurotoxicity. On the other hand, heparan... |
|
|
Anti-obesity effect of sulfated glucosamine by AMPK signal pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 47(10) , 2401-6, (2009) In this study, we investigated the effect of sulfated glucosamine (SGlc) on adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 adipocytes during differentiation of preadipocytes into adipocytes by measuring lipid accumulation and adipogenesis related factors. Treatment with SGlc reduced... |
|
|
Flavobacterium heparinum 6-O-sulphatase for N-substituted glucosamine 6-O-sulphate.
Eur. J. Biochem. 152 , 75, (1985) A specific glyco-6-O-sulphatase has been purified to homogeneity from Flavobacterium heparinum. The enzyme hydrolyses the 6-O-sulphates of 2-deoxy-2-sulphamido-6-O-sulpho-D-glucose (GlcNS-6S), 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-6-O-sulpho-D-glucose (GlcNAc-6S) and 2-amino-2... |
|
|
Heparan sulfate expression is affected by inflammatory stimuli in primary human endothelial cells.
Glycoconj. J. 29(1) , 67-76, (2012) In diabetes the endothelium is either chronically or transiently exposed to hyperglycemic conditions. In addition, endothelial dysfunction in diabetes is related to changes in the inflammatory response and the turnover of extracellular matrix. This study was ... |
|
|
The charged milieu: a major player in fertilization reactions.
Acta Histochem. 106(1) , 3-10, (2004) In previous studies, we have found that negatively charged, but not uncharged, amino acids and sugars block sea urchin fertilization. These studies were developed from modeling work in non-living systems using derivatized agarose beads that suggested that cha... |