Common binding sites for beta-amyloid fibrils and fibroblast growth factor-2 in heparan sulfate from human cerebral cortex.
B Lindahl, C Westling, G Giménez-Gallego, U Lindahl, M Salmivirta
Index: J. Biol. Chem. 274(43) , 30631-5, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Heparan sulfate found in the cerebral plaques of Alzheimer's disease binds to beta-amyloid (Abeta) fibrils. This interaction has been proposed to enhance fibril deposition and mediate Abeta-induced glia activation and neurotoxicity. On the other hand, heparan sulfate augments signaling of fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), a neuroprotective factor that antagonizes the neurotoxic effects of Abeta. We defined structures in heparan sulfate from human cerebral cortex that bind Abeta fibrils. The minimal binding site is found in N-sulfated hexasaccharide domains and contains critical 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid residues. By contrast, binding of Abeta monomers requires, in addition, 6-O-sulfate groups on glucosamine residues. The binding specificity of fibrillar Abeta is shared by FGF-2, and we here show that cerebral heparan sulfate domains selected for binding to Abeta-(1-40) fibrils bind also to FGF-2. These data suggest that neurotoxic and neuroprotective signals may converge by competing for the same binding sites on the heparan sulfate chain.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
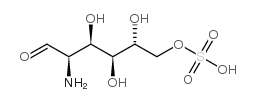 |
D-Glucosamine-6-sulfate
CAS:91674-26-9 |
C6H13NO8S |
|
Human ficolin-2 recognition versatility extended: an update ...
2014-12-20 [FEBS Lett. 588(24) , 4694-700, (2014)] |
|
Characteristics of the glmS ribozyme suggest only structural...
2006-04-01 [RNA 12 , 607 - 619, (2006)] |
|
The effects of glucosamine sulfate on intervertebral disc an...
2015-06-01 [Spine J. 15 , 1339-46, (2015)] |
|
Binding of heparin to antithrombin III: a chemical proof of ...
1988-08-15 [Carbohydr. Res. 179 , 163-72, (1988)] |
|
Anti-obesity effect of sulfated glucosamine by AMPK signal p...
2009-10-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 47(10) , 2401-6, (2009)] |